Catalase (PT0146R) PT® Rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8083
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;IP;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- Catalase
- Fields:
- >>Tryptophan metabolism;>>Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Carbon metabolism;>>FoxO signaling pathway;>>Peroxisome;>>Longevity regulating pathway;>>Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species;>>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases;>>Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species
- Gene Name:
- CAT
- Protein Name:
- Catalase
- Human Gene Id:
- 847
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P04040
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P24270
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal, rabbit, IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-1000,WB 1:1000-5000,IF 1:200-1000,ELISA 1:5000-20000,IP 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CAT;Catalase
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 60kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 60kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes catalase, a key antioxidant enzyme in the bodies defense against oxidative stress. Catalase is a heme enzyme that is present in the peroxisome of nearly all aerobic cells. Catalase converts the reactive oxygen species hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen and thereby mitigates the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide. Oxidative stress is hypothesized to play a role in the development of many chronic or late-onset diseases such as diabetes, asthma, Alzheimer's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancers. Polymorphisms in this gene have been associated with decreases in catalase activity but, to date, acatalasemia is the only disease known to be caused by this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:2 H(2)O(2) = O(2) + 2 H(2)O.,cofactor:Heme group.,cofactor:NADP.,disease:Defects in CAT are the cause of acatalasia (ACATLAS) [MIM:115500]; also known as acatalasemia. This disease is characterized by absence of catalase activity in red cells and is often associated with ulcerating oral lesions.,function:Occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide. Promotes growth of cells including T-cells, B-cells, myeloid leukemia cells, melanoma cells, mastocytoma cells and normal and transformed fibroblast cells.,online information:Catalase entry,PTM:The N-terminus is blocked.,similarity:Belongs to the catalase family.,subunit:Homotetramer.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm
- Expression:
- Brain,Cajal-Retzius cell,Erythrocyte,Eye,Fibroblast,Kidney,Liver,Placenta,Platelet,Skin,Uterus,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
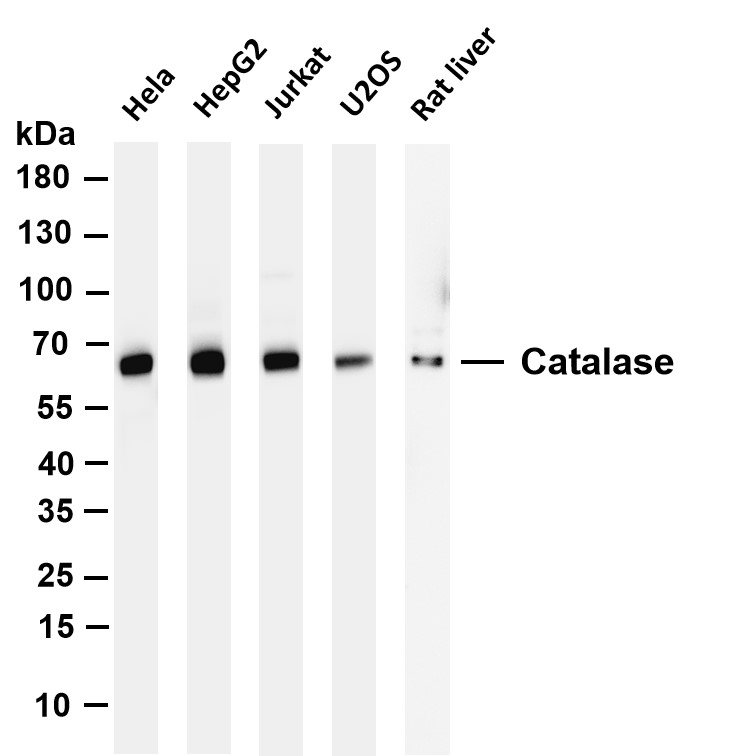
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-20% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-Catalase (PT0146R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: Hela Lane 2: HepG2 Lane 3: Jurkat Lane 4: U2OS Lane 5: Rat liver Predicted band size: 60kDa Observed band size: 60kDa
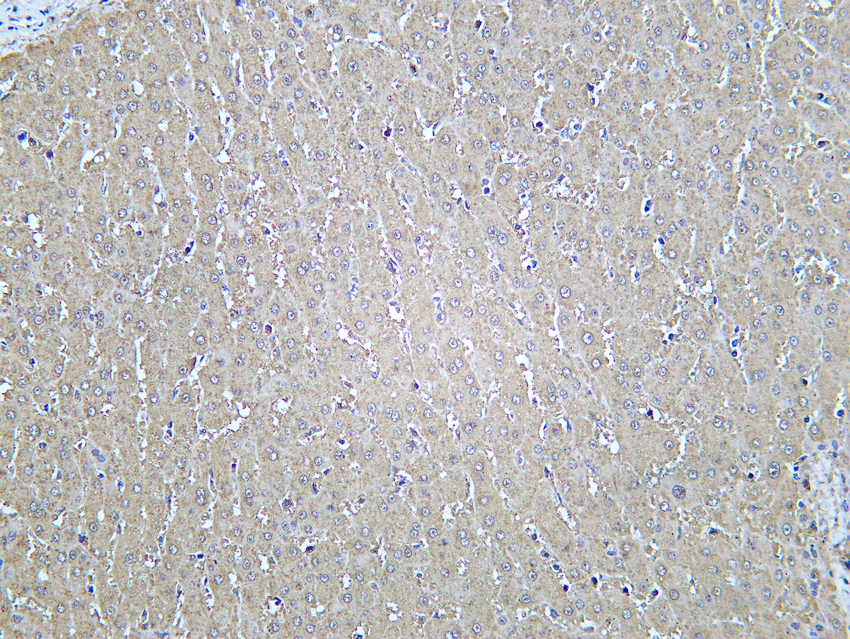
- Human liver was stained with Anti-Catalase (PT0146R) rabbit antibody
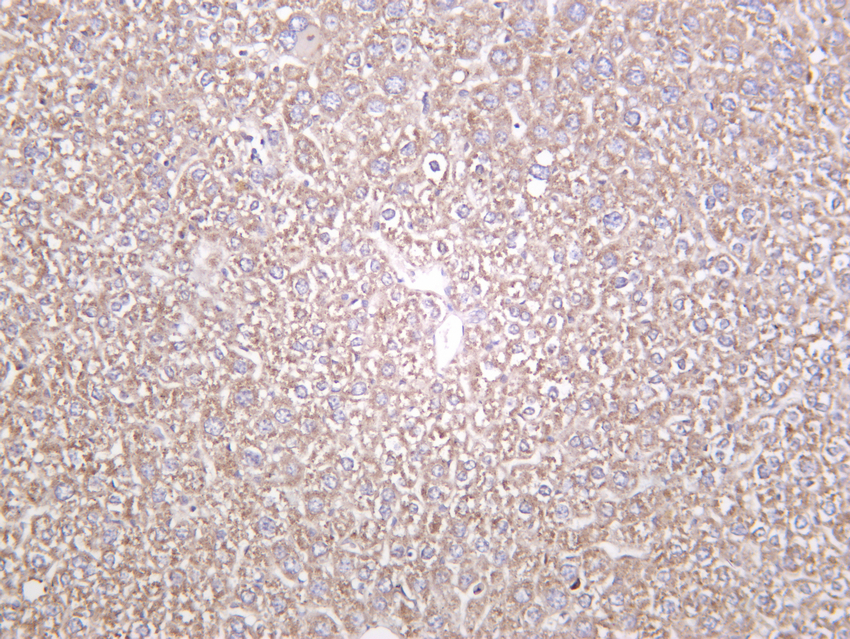
- Mouse liver was stained with Anti-Catalase (PT0146R) rabbit antibody
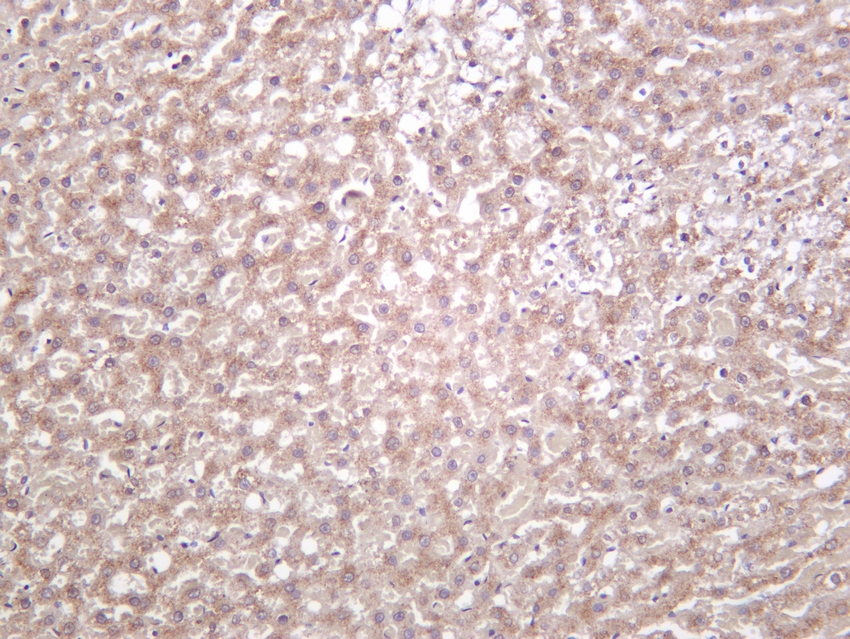
- Rat liver was stained with Anti-Catalase (PT0146R) rabbit antibody
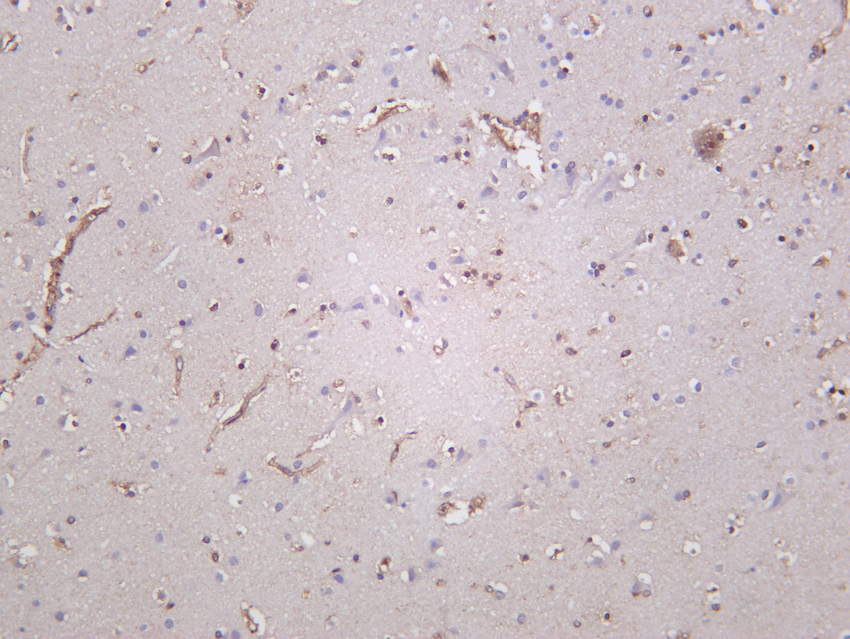
- Human brain was stained with Anti-Catalase (PT0146R) rabbit antibody



