Cleaved PARP1 (PT0046R) PT® Rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8021
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;IP;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human; Mouse; Rat;
- Target:
- PARP1
- Fields:
- >>Base excision repair;>>NF-kappa B signaling pathway;>>Apoptosis;>>Necroptosis;>>Diabetic cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- PARP1
- Protein Name:
- Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 142
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P09874
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P11103
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal, rabbit, IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-1000,WB 1:500-5000,IF 1:200-1000,ELISA 1:5000-20000,IP 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PARP1;ADPRT;PPOL;Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1;PARP-1;ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 1;ARTD1;NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase 1;ADPRT 1;Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 25kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 25kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a chromatin-associated enzyme, poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase, which modifies various nuclear proteins by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. The modification is dependent on DNA and is involved in the regulation of various important cellular processes such as differentiation, proliferation, and tumor transformation and also in the regulation of the molecular events involved in the recovery of cell from DNA damage. In addition, this enzyme may be the site of mutation in Fanconi anemia, and may participate in the pathophysiology of type I diabetes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:NAD(+) + (ADP-D-ribosyl)(n)-acceptor = nicotinamide + (ADP-D-ribosyl)(n+1)-acceptor.,function:Involved in the base excision repair (BER) pathway, by catalyzing the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of a limited number of acceptor proteins involved in chromatin architecture and in DNA metabolism. This modification follows DNA damages and appears as an obligatory step in a detection/signaling pathway leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks.,miscellaneous:The ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD(+) is transferred to an acceptor carboxyl group on a histone or the enzyme itself, and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units.,PTM:Phosphorylated by PRKDC. Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,PTM:Poly-ADP-ribosylated by PARP2.,similarity:Contains 1 BRCT
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic, Nuclear
- Expression:
- Brain,Colon carcinoma,Fibroblast,Lung,Ovarian carcinoma,Skin,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
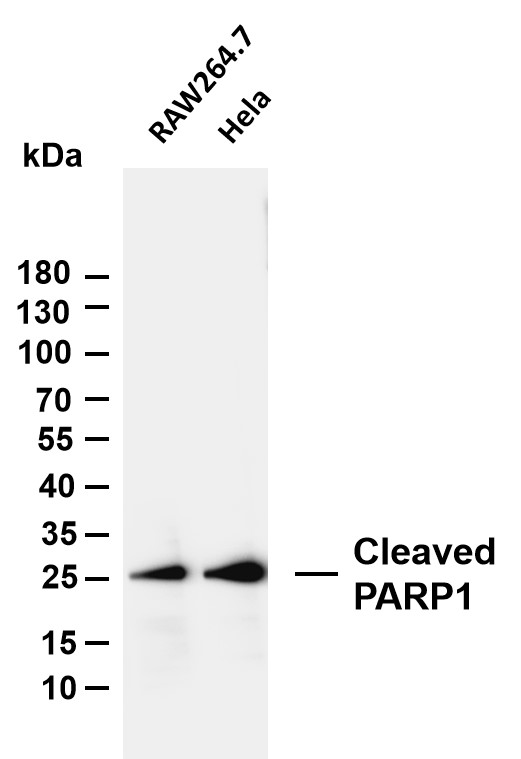
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-20% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-Cleaved PARP1 (PT0046R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: RAW264.7 Lane 2: Hela Predicted band size: 25kDa
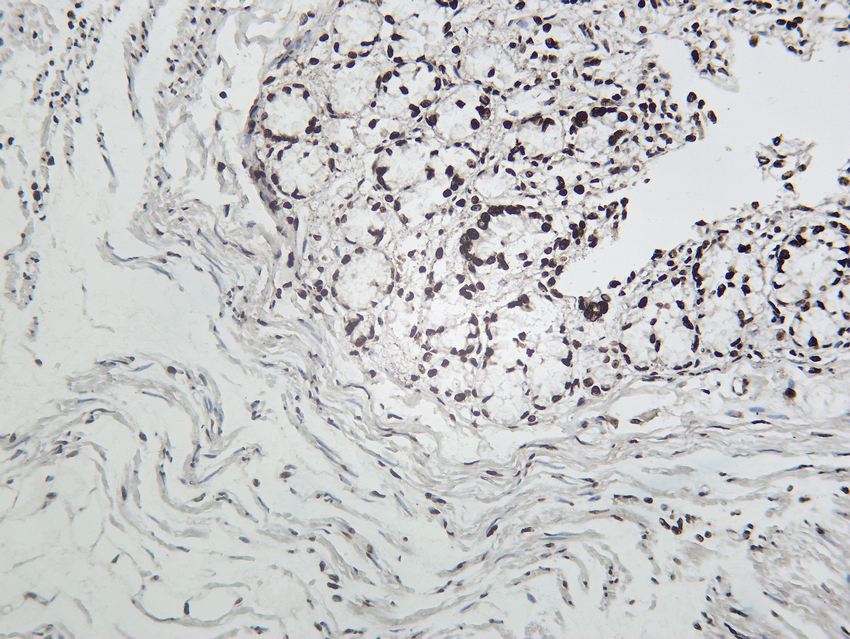
- Rat colon tissue was stained with Anti-Cleaved PARP1 (PT0046R) rabbit Antibody
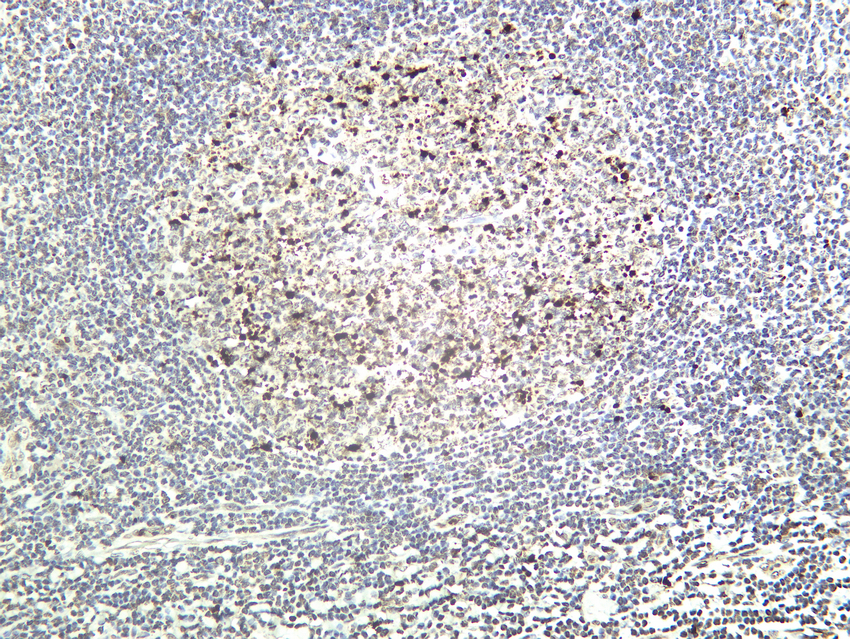
- Human tonsil tissue was stained with Anti-Cleaved PARP1 (PT0046R) rabbit Antibody



