β-actin (PT0022R) rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8010
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- Actin β
- Fields:
- >>Rap1 signaling pathway;>>Phagosome;>>Apoptosis;>>Hippo signaling pathway;>>Focal adhesion;>>Adherens junction;>>Tight junction;>>Platelet activation;>>Neutrophil extracellular trap formation;>>Leukocyte transendothelial migration;>>Thermogenesis;>>Regulation of actin cytoskeleton;>>Thyroid hormone signaling pathway;>>Oxytocin signaling pathway;>>Gastric acid secretion;>>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells;>>Vibrio cholerae infection;>>Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection;>>Shigellosis;>>Salmonella infection;>>Yersinia infection;>>Influenza A;>>Proteoglycans in cancer;>>Hepatocellular carcinoma;>>Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;>>Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy;>>Dilated cardiomyopathy;>>Viral myocarditis;>>Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- ACTB
- Protein Name:
- Actin cytoplasmic 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 60
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P60709
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 11461
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P60710
- Rat Gene Id:
- 81822
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P60711
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human protein. AA range:1-100
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal Rabbit IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 ELISA: 1:20000
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ACTB;Actin; cytoplasmic 1;Beta-actin;Actin β;β-Actin;Beta actin;B actin;actin Beta;
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 42kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 42kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes one of six different actin proteins. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure, and integrity. This actin is a major constituent of the contractile apparatus and one of the two nonmuscle cytoskeletal actins. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in ACTB are a cause of dystonia juvenile-onset (DYTJ) [MIM:607371]. DYTJ is a form of dystonia with juvenile onset. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contraction, often leading to abnormal postures. DYTJ patients manifest progressive, generalized, dopa-unresponsive dystonia, developmental malformations and sensory hearing loss.,function:Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.,miscellaneous:In vertebrates 3 main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta and gamma have been identified. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. The beta and gamma actins coexist in most cell types as components of the cytoskeleton and as mediators of internal cell motility.,similarity:Belongs to the
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Nucleus . Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs. .
- Expression:
- B-cell lymphoma,Brain,Cajal-Retzius cell,Eye,Fetal brain cortex,Foreskin,Hepatocellular car
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
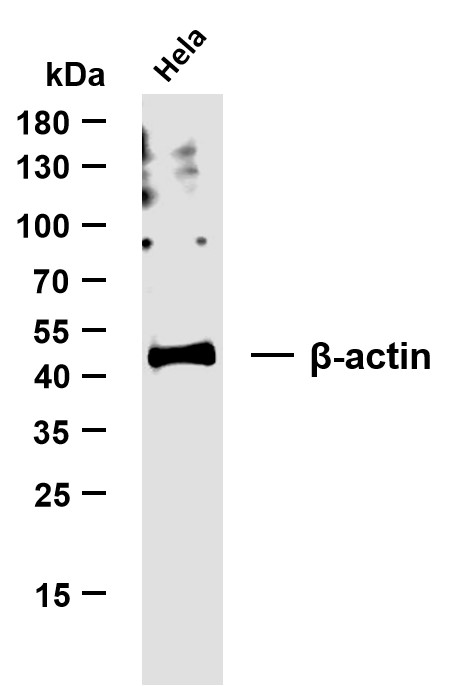
- Whole cell lysates were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-β-actin(PT0022R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1:Hela Predicted band size: 42kDa Observed band size: 42kDa



