GLUT-1 (ABT-GLUT1) mouse mAb (Ready to Use)
- Catalog No.:YM6583R
- Applications:IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- GLUT-1
- Fields:
- >>HIF-1 signaling pathway;>>Insulin secretion;>>Thyroid hormone signaling pathway;>>Adipocytokine signaling pathway;>>Glucagon signaling pathway;>>Insulin resistance;>>Bile secretion;>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Renal cell carcinoma;>>Central carbon metabolism in cancer;>>Diabetic cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- SLC2A1 GLUT1
- Protein Name:
- Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (Glucose transporter type 1, erythrocyte/brain) (GLUT-1) (HepG2 glucose transporter)
- Human Gene Id:
- 6513
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P11166
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human GLUT-1 AA range: 400-492
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human GLUT-1 protein.
- Formulation:
- The prediluted ready-to-use antibody is diluted in phosphate buffer saline containing stabilizing protein and 0.05% Proclin 300
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG2a, kappa
- Dilution:
- Ready to use for IHC
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- 2°C to 8°C/1 year
- Background:
- This gene encodes a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. The encoded protein is found primarily in the cell membrane and on the cell surface, where it can also function as a receptor for human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II. Mutations in this gene have been found in a family with paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesia. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SLC2A1 are the cause of autosomal dominant GLUT1 deficiency syndrome [MIM:606777]; also called blood-brain barrier glucose transport defect. This disease causes a defect in glucose transport across the blood-brain barrier. It is characterized by infantile seizures, delayed development, and acquired microcephaly.,disease:Defects in SLC2A1 are the cause of dystonia type 18 (DYT18) [MIM:612126]. DYT18 is an exercise-induced paroxysmal dystonia/dyskinesia. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contraction, often leading to abnormal postures. DYT18 is characterized by attacks of involuntary movements triggered by certain stimuli such as sudden movement or prolonged exercise. In some patients involuntary exertion-induced dystonic, choreoathetotic, and ballistic movements may be associated with macrocytic hemolytic anemia.,function:Facilitative g
- Subcellular Location:
- Membranous
- Expression:
- Detected in erythrocytes (at protein level). Expressed at variable levels in many human tissues.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Mouse kidney tissue was stained with Anti-GLUT-1 (ABT-GLUT1) Antibody

- Mouse kidney tissue was stained with Anti-GLUT-1 (ABT-GLUT1) Antibody
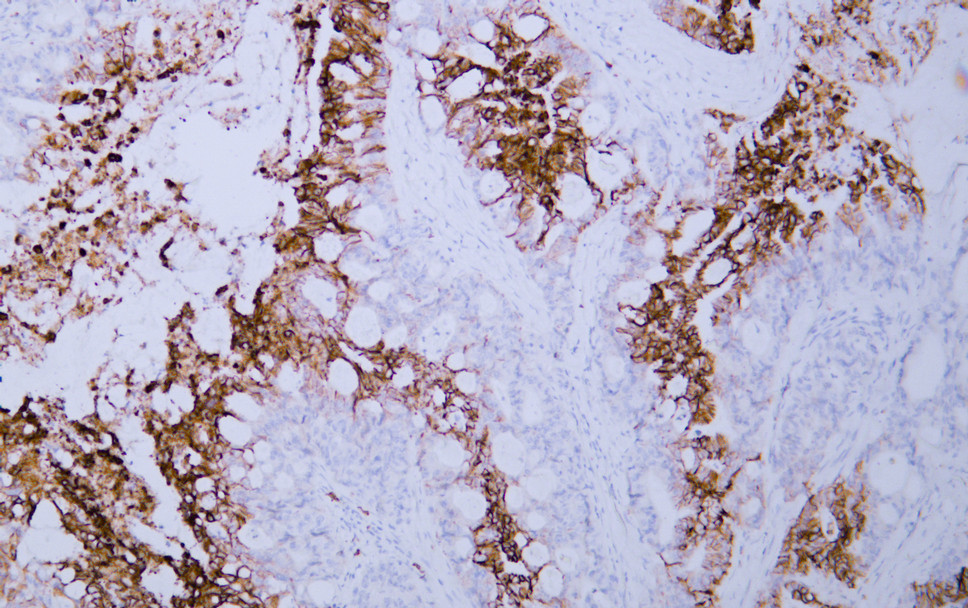
- Human colon carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-GLUT-1 (ABT-GLUT1) Antibody



