Cellular Apoptosis Susceptibility/CSE1L (PTR1397) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM4813
- Applications:WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- CAS
- Fields:
- >>Nucleocytoplasmic transport;>>Salmonella infection
- Gene Name:
- CSE1L
- Protein Name:
- Exportin-2
- Human Gene Id:
- 1434
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P55060
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9ERK4
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human protein.AA range:1-100
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of CSE1L.
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG3, kappa
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000. IF 1:100-500. ELISA 1:1000-5000
- Purification:
- Protein G
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CSE1L;CAS;XPO2;Exportin-2;Exp2;Cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein;Chromosome segregation 1-like protein;Importin-alpha re-exporter
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 110kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 110kD
- Background:
- Proteins that carry a nuclear localization signal (NLS) are transported into the nucleus by the importin-alpha/beta heterodimer. Importin-alpha binds the NLS, while importin-beta mediates translocation through the nuclear pore complex. After translocation, RanGTP binds importin-beta and displaces importin-alpha. Importin-alpha must then be returned to the cytoplasm, leaving the NLS protein behind. The protein encoded by this gene binds strongly to NLS-free importin-alpha, and this binding is released in the cytoplasm by the combined action of RANBP1 and RANGAP1. In addition, the encoded protein may play a role both in apoptosis and in cell proliferation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012],
- Function:
- function:Export receptor for importin-alpha. Mediates importin-alpha re-export from the nucleus to the cytoplasm after import substrates (cargos) have been released into the nucleoplasm. In the nucleus binds cooperatively to importin-alpha and to the GTPase Ran in its active GTP-bound form. Docking of this trimeric complex to the nuclear pore complex (NPC) is mediated through binding to nucleoporins. Upon transit of a nuclear export complex into the cytoplasm, disassembling of the complex and hydrolysis of Ran-GTP to Ran-GDP (induced by RANBP1 and RANGAP1, respectively) cause release of the importin-alpha from the export receptor. CSE1L/XPO2 then return to the nuclear compartment and mediate another round of transport. The directionality of nuclear export is thought to be conferred by an asymmetric distribution of the GTP- and GDP-bound forms of Ran between the cytoplasm and nucleus.,sim
- Subcellular Location:
- 0
- Expression:
- Detected in brain, placenta, ovary, testis and trachea (at protein level) (PubMed:10331944). Widely expressed (PubMed:10331944). Highly expressed in testis and in proliferating cells (PubMed:7479798,PubMed:10331944).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
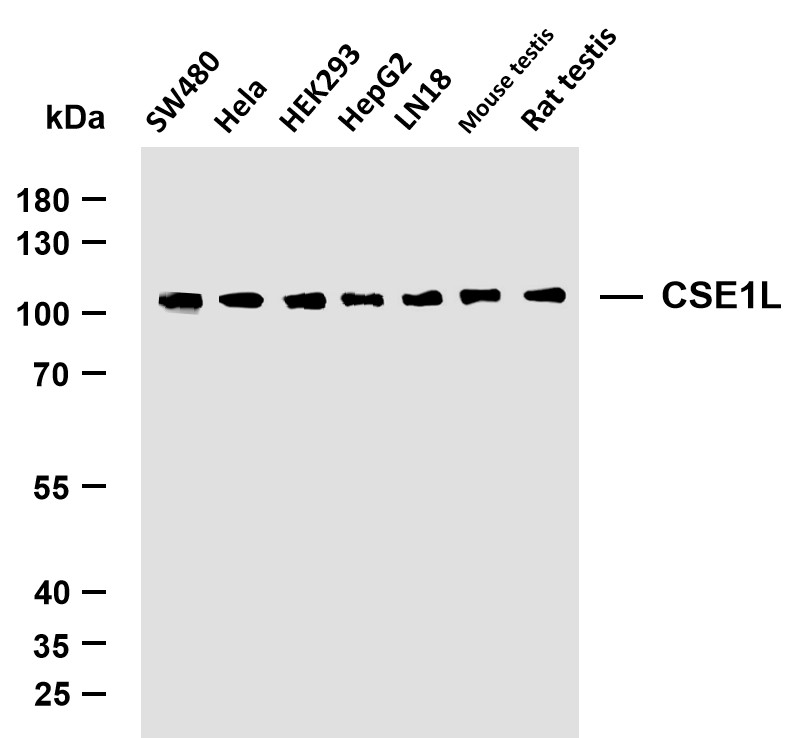
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-20% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-CSE1L (PTR1397) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: SW480 Lane 2: Hela Lane 3: HEK293 Lane 4: HepG2 Lane 5: LN18 Lane 6: Mouse testis Lane 7: Rat testis



