SRA1 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0595
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- SRA1
- Gene Name:
- SRA1
- Protein Name:
- Steroid receptor RNA activator 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 10011
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9HD15
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q80VJ2
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of SRA1 expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- SRA1 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of SRA1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SRA1;PP7684;Steroid receptor RNA activator 1;Steroid receptor RNA activator protein;SRAP
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 24kD
- References:
- 1. Rainer B. Lanz, Steven S. Chua, Niall Barron. Mol. Cell. Biol, Oct 2003; 23: 7163 - 7176.
2. Shilpa Chooniedass-Kothari, Mohammad Kariminia Hamedani, Sandy Troup. Int J Cancer. 2006 Feb 15;118(
- Background:
- Both long non-coding and protein-coding RNAs are transcribed from this gene, and they represent alternatively spliced transcript variants. This gene was initially defined as a non-coding RNA, which is a coactivator for several nuclear receptors (NRs) and is associated with breast cancer. It has now been found that this gene is involved in the regulation of many NR and non-NR activities, including metabolism, adipogenesis and chromatin organization. The long non-coding RNA transcripts interact with a variety of proteins, including the protein encoded by this gene. The encoded protein acts as a transcriptional repressor by binding to the non-coding RNA. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012],
- Function:
- function:Functional RNA which acts as a transcriptional coactivator that selectively enhances steroid receptor-mediated transactivation ligand-independently through a mechanism involving the modulating N-terminal domain (AF-1) of steroid receptors. Also mediates transcriptional coactivation of steroid receptors ligand-dependently through the steroid-binding domain (AF-2). Enhances cellular proliferation and differentiation and promotes apoptosis in vivo. May play a role in tumorigenesis.,miscellaneous:Appears to be the first example of a new class of functional RNAs also able to encode a protein.,similarity:Belongs to the SRA1 family.,subunit:SRA1 RNA exists in a ribonucleoprotein complex containing NCOA1. The RNA also forms a complex with PUS1 and RARG in the nucleus. Interacts with AR.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in liver and skeletal muscle and to a lesser extent in brain. Als
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Cytoplasm .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in liver and skeletal muscle and to a lesser extent in brain. Also expressed in both normal and tumorigenic breast epithelial cell lines. Significantly up-regulated in human tumors of the breast, ovary, and uterus.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using SRA1 Monoclonal Antibody against truncated SRA recombinant protein (1), human ovary cancer tissue lysate (2) and A431 cell lysate (3).
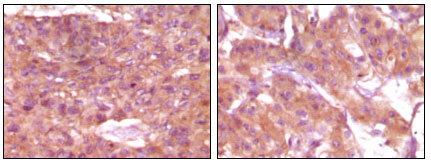
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human skin carcinoma (left) and breast carcinoma (right), showing cytoplasmic and membrane localization with DAB staining using SRA1 Monoclonal Antibody.


