PLZF Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0523
- Applications:WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- PLZF
- Fields:
- >>Pathways in cancer;>>Transcriptional misregulation in cancer;>>Acute myeloid leukemia
- Gene Name:
- ZBTB16
- Protein Name:
- Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16
- Human Gene Id:
- 7704
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q05516
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human PLZF expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- PLZF Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PLZF protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ZBTB16;PLZF;ZNF145;Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16;Promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein;Zinc finger protein 145;Zinc finger protein PLZF
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 74kD
- References:
- 1. Cancer Res. 2008 Apr 15;68(8):2745-54
2. Immunity. 2008 Sep 19;29(3):391-403.
- Background:
- This gene is a member of the Krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family and encodes a zinc finger transcription factor that contains nine Kruppel-type zinc finger domains at the carboxyl terminus. This protein is located in the nucleus, is involved in cell cycle progression, and interacts with a histone deacetylase. Specific instances of aberrant gene rearrangement at this locus have been associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:A chromosomal aberration involving ZBTB16 may be a cause of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Translocation t(11;17)(q32;q21) with RARA.,disease:Defects in ZBTB16 are the cause of skeletal defects genital hypoplasia and mental retardation [MIM:612447]. The disorder is characterized by mental retardation, craniofacial dysmorphism, microcephaly and short stature. Additional features include absence of the thumbs, hypoplasia of the radii and ulnae, additional vertebrae and ribs, retarded bone age and genital hypoplasia.,function:Probable transcription factor. May play a role in myeloid maturation and in the development and/or maintenance of other differentiated tissues. Probable substrate-recognition component of an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins.,induction:By retinoic acid.,pathway:Pr
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Nucleus, nuclear body .
- Expression:
- Within the hematopoietic system, PLZF is expressed in bone marrow, early myeloid cell lines and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Also expressed in the ovary, and at lower levels, in the kidney and lung.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using PLZF Monoclonal Antibody against HeLa (1) cell lysate.
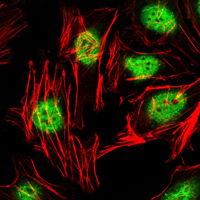
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Hela cells using PLZF Monoclonal Antibody (green). Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin.



