I-FABP Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0352
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;FCM;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- I-FABP
- Fields:
- >>PPAR signaling pathway;>>Fat digestion and absorption
- Gene Name:
- FABP2
- Protein Name:
- Fatty acid-binding protein, intestinal
- Human Gene Id:
- 2169
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P12104
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P55050
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human I-FABP expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- I-FABP Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of I-FABP protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. Flow cytometry: 1:200 - 1:400. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- FABP2;FABPI;Fatty acid-binding protein; intestinal;Fatty acid-binding protein 2;Intestinal-type fatty acid-binding protein;I-FABP
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 15kD
- References:
- 1. Yamada, K. et al. (1997) Diabetologia. 40(6):706-10
2. Georgopoulos, A. et al. (2000)85(9):3155-60
3. Kim, CH. et al. (2001) Metabolism. 50(4):473-6
4. Fisher, E. et al. (2006) Horm Met
- Background:
- The intracellular fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) belong to a multigene family with nearly twenty identified members. FABPs are divided into at least three distinct types, namely the hepatic-, intestinal- and cardiac-type. They form 14-15 kDa proteins and are thought to participate in the uptake, intracellular metabolism and/or transport of long-chain fatty acids. They may also be responsible in the modulation of cell growth and proliferation. Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein 2 gene contains four exons and is an abundant cytosolic protein in small intestine epithelial cells. This gene has a polymorphism at codon 54 that identified an alanine-encoding allele and a threonine-encoding allele. Thr-54 protein is associated with increased fat oxidation and insulin resistance. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:Forms a beta-barrel structure that accommodates the hydrophobic ligand in its interior.,function:FABP are thought to play a role in the intracellular transport of long-chain fatty acids and their acyl-CoA esters. FABP2 is probably involved in triglyceride-rich lipoprotein synthesis. Binds saturated long-chain fatty acids with a high affinity, but binds with a lower affinity to unsaturated long-chain fatty acids. FABP2 may also help maintain energy homeostasis by functioning as a lipid sensor.,induction:By EGF.,similarity:Belongs to the calycin superfamily. Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family.,tissue specificity:Expressed in the small intestine and at much lower levels in the large intestine. Highest expression levels in the jejunum.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm.
- Expression:
- Expressed in the small intestine and at much lower levels in the large intestine. Highest expression levels in the jejunum.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
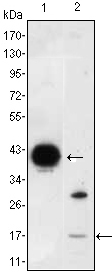
- Western Blot analysis using I-FABP Monoclonal Antibody against FABP2-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (1) cell lysate and LOVO (2) cell lysate.
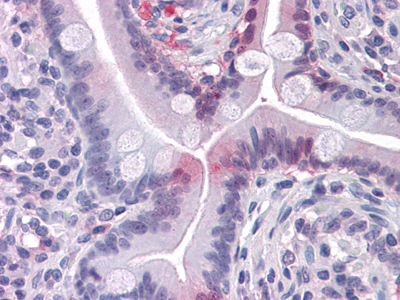
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human Small Intestine tissues with AEC staining using I-FABP Monoclonal Antibody.

- Immunofluorescence analysis of 3T3-L1 cells using I-FABP Monoclonal Antibody (green). Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye. Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin.

- Flow cytometric analysis of LOVO cells using I-FABP Monoclonal Antibody (green) and negative control (purple).



