Hck Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0326
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Hck
- Fields:
- >>Chemokine signaling pathway;>>Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis;>>Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Gene Name:
- HCK
- Protein Name:
- Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK
- Human Gene Id:
- 3055
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P08631
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P08103
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of Hck expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- Hck Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Hck protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- HCK;Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK;Hematopoietic cell kinase;Hemopoietic cell kinase;p59-HCK/p60-HCK;p59Hck;p61Hck
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 60kD
- References:
- 1. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007 Aug;41(7):667-70.
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Src family of tyrosine kinases. This protein is primarily hemopoietic, particularly in cells of the myeloid and B-lymphoid lineages. It may help couple the Fc receptor to the activation of the respiratory burst. In addition, it may play a role in neutrophil migration and in the degranulation of neutrophils. Multiple isoforms with different subcellular distributions are produced due to both alternative splicing and the use of alternative translation initiation codons, including a non-AUG (CUG) codon. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,domain:The SH3 domain mediates binding to HIV-1 Nef.,function:May serve as part of a signaling pathway coupling the Fc receptor to the activation of the respiratory burst. May also contribute to neutrophil migration and may regulate the degranulation process of neutrophils.,PTM:Isoform p59-HCK contains a N-myristoyl glycine at position 3 (By similarity). Isoform p59-HCK contains a S-palmitoyl cysteine at position 3.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. SRC subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 1 SH2 domain.,similarity:Contains 1 SH3 domain.,subunit:May interact (via SH3 domain) with HIV-1 Nef and Vif. This interaction would stimulates its tyrosine-kinase activity. Interacts (via SH3 domain) with HEV ORF3 protein.,tissu
- Subcellular Location:
- [Isoform 1]: Lysosome. Membrane; Lipid-anchor. Cell projection, podosome membrane; Lipid-anchor. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Associated with specialized secretory lysosomes called azurophil granules. At least half of this isoform is found in the cytoplasm, some of this fraction is myristoylated.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane ; Lipid-anchor . Membrane, caveola ; Lipid-anchor . Cell junction, focal adhesion . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Golgi apparatus . Cytoplasmic vesicle . Lysosome . Nucleus . 20% of this isoform is associated with caveolae. Localization at the cell membrane and at caveolae requires palmitoylation at Cys-3. Colocalizes with the actin cytoskeleton at focal adhesions.; Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle. Cytoplasm, cytosol.
- Expression:
- Detected in monocytes and neutrophils (at protein level). Expressed predominantly in cells of the myeloid and B-lymphoid lineages. Highly expressed in granulocytes. Detected in tonsil.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
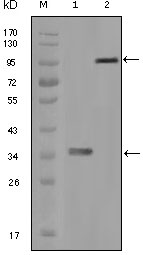
- Western Blot analysis using Hck Monoclonal Antibody against truncated HCK recombinant protein (1) and full-length HCK-GFP transfected CHO-K1 cell lysate (2).
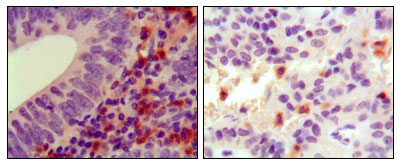
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon cancer (left) and ancreas cancer (right), showing cytoplasmic localization with DAB staining using Hck Monoclonal Antibody.



