Human FGF-Basic ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KE1016
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Gene Name:
- FGF2
- Protein Name:
- Fibroblast growth factor 2
- Human Gene Id:
- 2247
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P09038
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P15655
- Specificity:
- Sample Type for Cell Culture Supernates, Cell lysates, Tissue Lysates, Serum, EDTA Plasma, Heparin Plasma
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- FGF2;FGFB;Fibroblast growth factor 2;FGF-2;Basic fibroblast growth factor;bFGF;Heparin-binding growth factor 2;HBGF-2
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- function:The heparin-binding growth factors are angiogenic agents in vivo and are potent mitogens for a variety of cell types in vitro. There are differences in the tissue distribution and concentration of these 2 growth factors.,miscellaneous:This protein binds heparin more strongly than does aFGF.,PTM:Several N-termini starting at positions 48, 54, 47 and 65 have been identified by direct sequencing.,sequence caution:Unusual initiator. The initiator methionine is coded by a non-canonical CTG leucine codon.,similarity:Belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family.,subunit:Monomer. Interacts with CSPG4 and FGFBP1. Found in a complex with FGFBP1, FGF1 and FGF2.,tissue specificity:Expressed in granulosa and cumulus cells.,
- Function:
- protein import into nucleus, translocation, MAPKKK cascade, activation of MAPKK activity, activation of MAPK activity,nuclear translocation of MAPK, angiogenesis, regulation of cell growth, blood vessel development, cell fate specification, induction of an organ, regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, vasculature development, sprouting angiogenesis, cell migration during sprouting angiogenesis, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, protein amino acid phosphorylation, protein targeting, protein import into nucleus, steroid biosynthetic process, C21-steroid hormone biosynthetic process, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process,intracellular protein transport, nucleocytoplasmic transport, apoptosis, cell motion, chemotaxis, cell surface re
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted . Nucleus . Exported from cells by an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)/Golgi-independent mechanism. Unconventional secretion of FGF2 occurs by direct translocation across the plasma membrane (PubMed:20230531). Binding of exogenous FGF2 to FGFR facilitates endocytosis followed by translocation of FGF2 across endosomal membrane into the cytosol (PubMed:22321063). Nuclear import from the cytosol requires the classical nuclear import machinery, involving proteins KPNA1 and KPNB1, as well as CEP57 (PubMed:22321063). .
- Expression:
- Expressed in granulosa and cumulus cells. Expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not in non-cancerous liver tissue.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
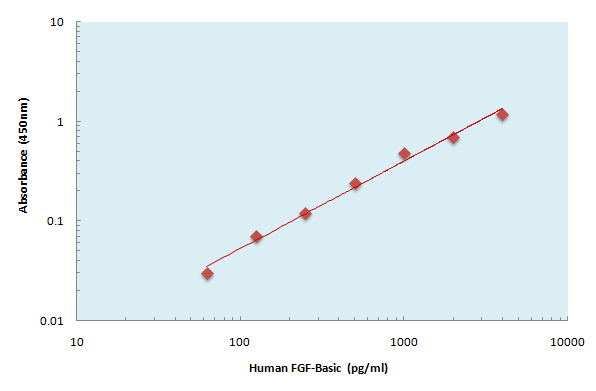
- The Human FGF-Basic ELISA Kit allows for the detection and quantification of endogenous levels of natural and/or recombinant Human FGF-Basic proteins within the range of 63-400 pg/ml.



