Perforin (ABT236R) IHC kit
- Catalog No.:IHCM7190
- Applications:IHC
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- Perforin
- Fields:
- >>Apoptosis;>>Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity;>>Type I diabetes mellitus;>>Autoimmune thyroid disease;>>Allograft rejection;>>Graft-versus-host disease;>>Viral myocarditis
- Gene Name:
- PRF1
- Protein Name:
- Cytolysin;FLH2;HPLH2;Lymphocyte pore-forming protein;P1;PERF_HUMAN;perforin 1 (pore forming protein);Perforin 1;Perforin-1;PFP;PGFL;PIGF;PIGF-2;PLGF;Pore forming protein;prf1;SHGC-10760
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P14222
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P10820
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P35763
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Perforin AA range:1-100
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of Perforin
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Rabbit IgG1, Kappa
- Purification:
- Recombinant Expression and Affinity purified
- Storage Stability:
- 2°C to 8°C/1 year
- Other Name:
- Cytolysin;FLH2;HPLH2;Lymphocyte pore-forming protein;P1;PERF_HUMAN;perforin 1 (pore forming protein);Perforin 1;Perforin-1;PFP;PGFL;PIGF;PIGF-2;PLGF;Pore forming protein;prf1;SHGC-10760
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene has structural and functional similarities to complement component 9 (C9). Like C9, this protein creates transmembrane tubules and is capable of lysing non-specifically a variety of target cells. This protein is one of the main cytolytic proteins of cytolytic granules, and it is known to be a key effector molecule for T-cell- and natural killer-cell-mediated cytolysis. Defects in this gene cause familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 2 (HPLH2), a rare and lethal autosomal recessive disorder of early childhood. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in PRF1 are the cause of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 2 (FHL2) [MIM:603553]; also known as HPLH2. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) is a genetically heterogeneous, rare autosomal recessive disorder. It is characterized by immune dysregulation with hypercytokinemia and defective natural killer cell function. The clinical features of the disease include fever, hepatosplenomegaly, cytopenia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypofibrinogenemia, and neurological abnormalities ranging from irritability and hypotonia to seizures, cranial nerve deficits, and ataxia. Hemophagocytosis is a prominent feature of the disease, and a non-malignant infiltration of macrophages and activated T lymphocytes in lymph nodes, spleen, and other organs is also found.,function:In the presence of calcium, perforin polymerizes into transmembrane tubules and is capable of lys
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic, Membranous
- Expression:
- Spleen
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Human spleen tissue was stained with anti-Perforin (ABT236R) rabbit Antibody
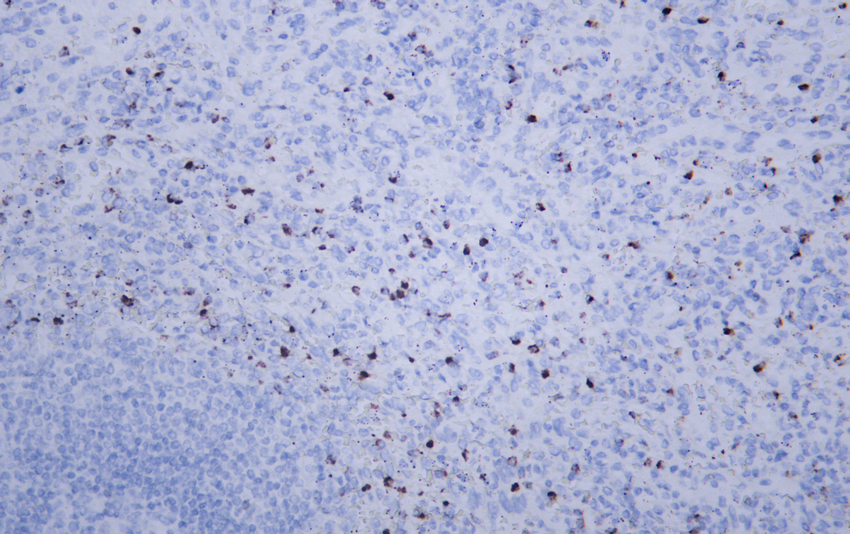
- Human spleen tissue was stained with anti-Perforin (ABT236R) rabbit Antibody



