Cytokeratin 20 (ABT044) IHC kit
- Catalog No.:IHCM6866
- Applications:IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- Cytokeratin 20
- Fields:
- >>Estrogen signaling pathway;>>Staphylococcus aureus infection
- Gene Name:
- KRT20
- Protein Name:
- Cytokeratin-20
- Human Gene Id:
- 54474
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P35900
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human CK20 AA range: 300-424
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human CK20 protein, and shows no cross reaction with CK1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 13, 14, 15, 17, 18.
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG2b, kappa
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- 2°C to 8°C/1 year
- Other Name:
- Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 20 (Cytokeratin-20;CK-20;Keratin-20;K20;Protein IT)
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin family. The keratins are intermediate filament proteins responsible for the structural integrity of epithelial cells and are subdivided into cytokeratins and hair keratins. The type I cytokeratins consist of acidic proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains. This cytokeratin is a major cellular protein of mature enterocytes and goblet cells and is specifically expressed in the gastric and intestinal mucosa. The type I cytokeratin genes are clustered in a region of chromosome 17q12-q21. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- developmental stage:First detected at embryonic week 8 in individual 'converted' simple epithelial cells of the developing intestinal mucosa. In later fetal stages, synthesis extends over most goblet cells and a variable number of villus enterocytes. In the developing gastric and intestinal mucosa, expressed in all enterocytes and goblet cells as well as certain 'low-differentiated' columnar cells, whereas the neuroendocrine and Paneth cells are negative.,function:Plays a significant role in maintaining keratin filament organization in intestinal epithelia. When phosphorylated, plays a role in the secretion of mucin in the small intestine.,miscellaneous:There are two types of cytoskeletal and microfibrillar keratin: I (acidic; 40-55 kDa) and II (neutral to basic; 56-70 kDa).,PTM:Hyperphosphorylation at Ser-13 occurs during the early stages of apoptosis but becomes less prominent during t
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic, Membranous
- Expression:
- Expressed predominantly in the intestinal epithelium. Expressed in luminal cells of colonic mucosa. Also expressed in the Merkel cells of keratinized oral mucosa; specifically at the tips of some rete ridges of the gingival mucosa, in the basal layer of the palatal mucosa and in the taste buds of lingual mucosa.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
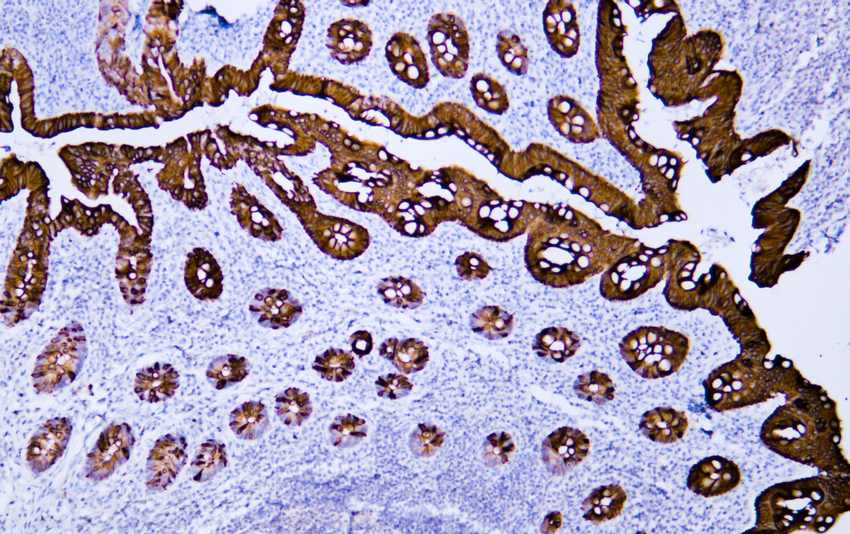
- Human appendix tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 20 (ABT044) Antibody
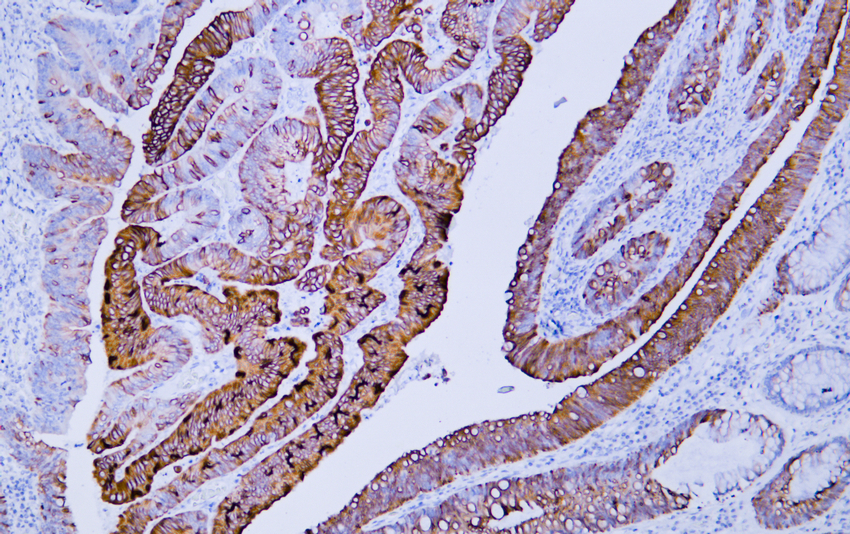
- Human colon carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 20 (ABT044) Antibody
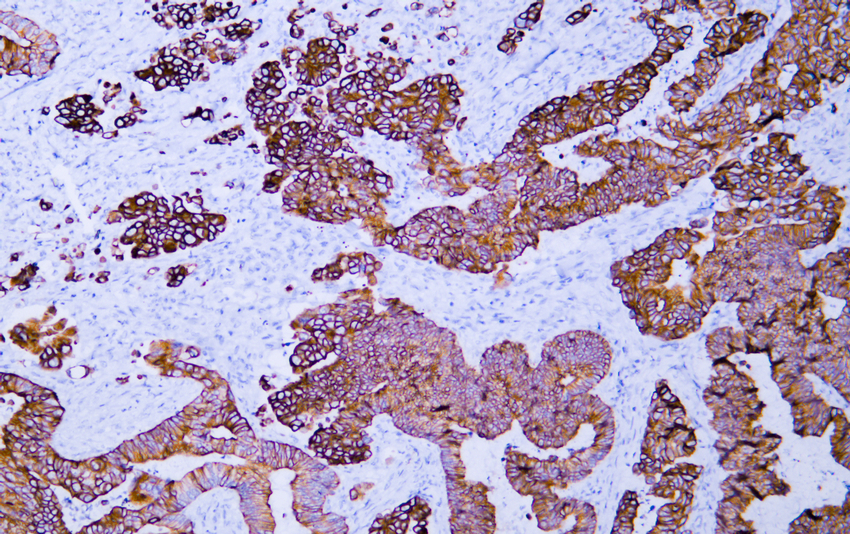
- Human rectal carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 20 (ABT044) Antibody



