KPB2 rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YT6905
- Applications:WB;IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- KPB2
- Fields:
- >>Calcium signaling pathway;>>Insulin signaling pathway;>>Glucagon signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- PHKA2 PHKLA PYK
- Protein Name:
- KPB2
- Human Gene Id:
- 5256
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P46019
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 110094
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8BWJ3
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human KPB2 AA range: 911-961
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of KPB2 at Human/Mouse
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:50-300
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 136kD
- Background:
- Phosphorylase kinase is a polymer of 16 subunits, four each of alpha, beta, gamma and delta. The alpha subunit includes the skeletal muscle and hepatic isoforms, and the hepatic isoform is encoded by this gene. The beta subunit is the same in both the muscle and hepatic isoforms, and encoded by one gene. The gamma subunit also includes the skeletal muscle and hepatic isoforms, which are encoded by two different genes. The delta subunit is a calmodulin and can be encoded by three different genes. The gamma subunits contain the active site of the enzyme, whereas the alpha and beta subunits have regulatory functions controlled by phosphorylation. The delta subunit mediates the dependence of the enzyme on calcium concentration. Mutations in this gene cause glycogen storage disease type 9A, also known as X-linked liver glycogenosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been reported, but the full-length nature of these variants has not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in PHKA2 are the cause of glycogen storage disease type 9A (GSD9A) [MIM:306000]; also known as X-linked liver glycogenosis (XLG). GSD9A is a metabolic disorder resulting in a mild glycogenosis with clinical symptoms that include hepatomegaly, growth retardation, muscle weakness, elevation of glutamate-pyruvate transaminase and glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and fasting hyperketosis. Two subtypes are known: type 1 or classic type, and type 2 or variant type. The variant type is characterized mainly by enlarged liver and growth retardation; patients do not show in vitro enzymatic deficiency of phosphorylase kinase. Unlike other glycogenosis diseases, GSD9A is generally a benign condition. Patients improve with age and are often asymptomatic as adults. Accurate diagnosis is therefore also of prognostic interest.,enzyme regula
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Lipid-anchor ; Cytoplasmic side .
- Expression:
- Predominantly expressed in liver and other non-muscle tissues.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western blot analysis of lysates from MCF-7 cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night
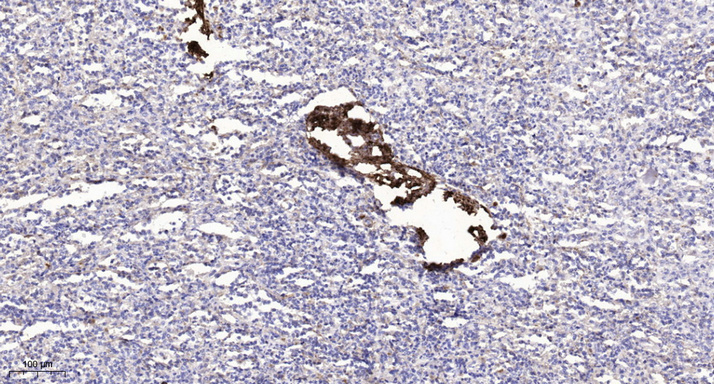
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human spleen. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



