GGT1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5266
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- GGT1
- Fields:
- >>Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism;>>Glutathione metabolism;>>Arachidonic acid metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways
- Gene Name:
- GGT1
- Protein Name:
- Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 2678
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P19440
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q60928
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the N-terminal region of human GGT1. AA range:21-70
- Specificity:
- GGT1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of GGT1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC: 1:100-300 ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GGT1;GGT;Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase 1;GGT 1;Gamma-glutamyltransferase 1;Glutathione hydrolase 1;Leukotriene-C4 hydrolase;CD224
- Observed Band(KD):
- 61kD
- Background:
- The enzyme encoded by this gene is a type I gamma-glutamyltransferase that catalyzes the transfer of the glutamyl moiety of glutathione to a variety of amino acids and dipeptide acceptors. The enzyme is composed of a heavy chain and a light chain, which are derived from a single precursor protein. It is expressed in tissues involved in absorption and secretion and may contribute to the etiology of diabetes and other metabolic disorders. Multiple alternatively spliced variants have been identified. There are a number of related genes present on chromosomes 20 and 22, and putative pseudogenes for this gene on chromosomes 2, 13, and 22. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:(5-L-glutamyl)-peptide + an amino acid = peptide + 5-L-glutamyl amino acid.,disease:Defects in GGT1 are a cause of glutathionuria [MIM:231950]; also known as gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase deficiency. It is an autosomal recessive disease.,function:Initiates extracellular glutathione (GSH) breakdown, provides cells with a local cysteine supply and contributes to maintain intracelular GSH level. It is part of the cell antioxidant defense mechanism. Catalyzes the transfer of the glutamyl moiety of glutathione to amino acids and dipeptide acceptors. Alternatively, glutathione can be hydrolyzed to give Cys-Gly and gamma glutamate. Isoform 3 seems to be inactive.,function:Initiates extracellular glutathione (GSH) breakdown; catalyzes the transfer of the glutamyl moiety of glutathione to amino acids and dipeptide acceptors.,miscellaneous:Corresponds to the light chain of other
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Detected in fetal and adult kidney and liver, adult pancreas, stomach, intestine, placenta and lung. There are several other tissue-specific forms that arise from alternative promoter usage but that produce the same protein.; [Isoform 3]: Lung-specific.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
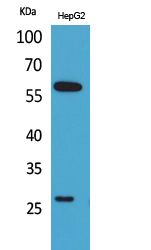
- Western Blot analysis of HepG2 cells using GGT1 Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
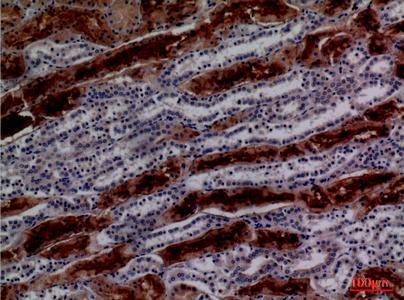
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human-kidney, antibody was diluted at 1:100
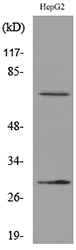
- Western blot analysis of lysate from HepG2 cells, using GGT1 Antibody.



