Hox-A1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT2208
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Hox-A1
- Fields:
- >>Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells
- Gene Name:
- HOXA1
- Protein Name:
- Homeobox protein Hox-A1
- Human Gene Id:
- 3198
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P49639
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P09022
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25607
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- O08656
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human HOXA1. AA range:171-220
- Specificity:
- Hox-A1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Hox-A1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- HOXA1;HOX1F;Homeobox protein Hox-A1;Homeobox protein Hox-1F
- Observed Band(KD):
- 37kD
- Background:
- In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. The encoded protein may be involved in the placement of hindbrain segments in the proper location along the anterior-posterior axis during development. Two transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene, with only one of the isoforms containing the homeodomain region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in HOXA1 are the cause of Athabaskan brainstem dysgenesis syndrome (ABSD) [MIM:601536]; also known as Narvajo brainstem syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by horizontal gaze palsy, sensorineural deafness, central hypoventilation, and developmental delay. Some patients had swallowing dysfunction, vocal cord paralysis, facial paresis, seizures, and cardiac outflow tract anomalies.,disease:Defects in HOXA1 are the cause of Bosley-Salih-Alorainy syndrome (BSAS) [MIM:601536]. Affected individuals show horizontal gaze abnormalities, deafness, facial weakness, vascular malformations of the internal carotid arteries and cardiac outflow trac. Some patients manifest mental retardation and autism spectrum disorder. In contrast to individuals with ABSD, central hypoventilation is not observed in individuals with BSAS.,function:Sequence-specific transcription factor which is par
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus .
- Expression:
- Ovary,Skin,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
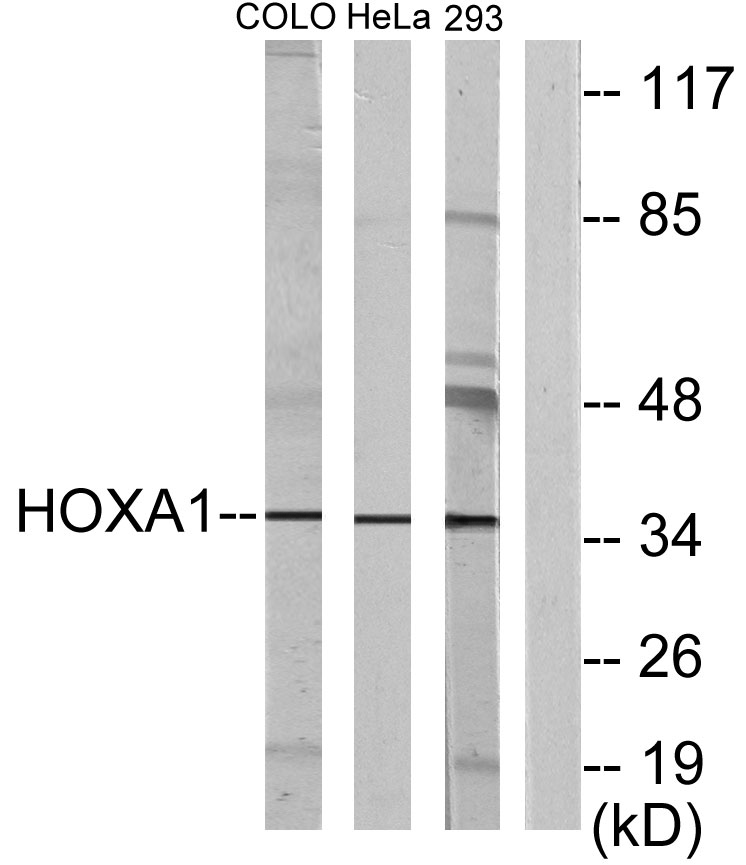
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa, COLO, and 293 cells, using HOXA1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
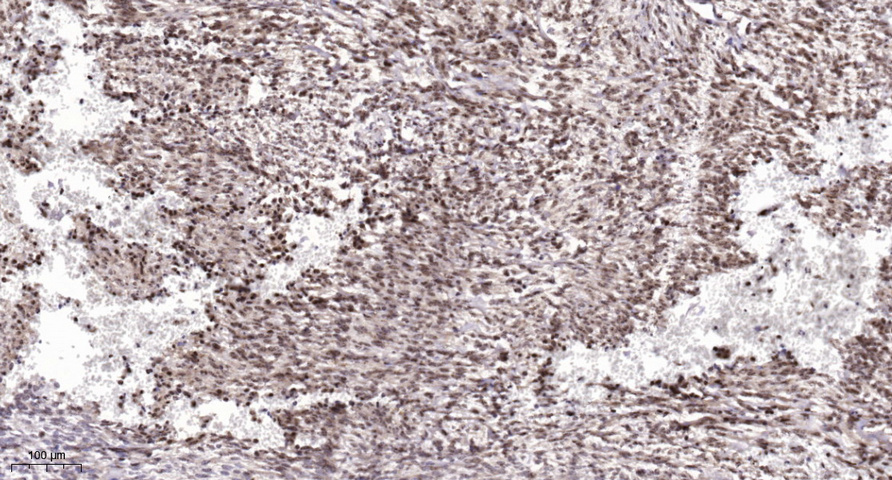
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human Colon cancer. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



