GFAP (PT0298R) rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8172
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;IP;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human; Mouse; Rat;
- Target:
- GFAP
- Fields:
- >>JAK-STAT signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- GFAP
- Protein Name:
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- Human Gene Id:
- 2670
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P14136
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14580
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P03995
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24387
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P47819
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal, rabbit, IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-1:1000,WB 1:1000-1:5000,IF 1:200-1:1000,ELISA 1:5000-1:20000,IP 1:50-1:200,
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GFAP;Glial fibrillary acidic protein;GFAP
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 50kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 50kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes one of the major intermediate filament proteins of mature astrocytes. It is used as a marker to distinguish astrocytes from other glial cells during development. Mutations in this gene cause Alexander disease, a rare disorder of astrocytes in the central nervous system. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008],
- Function:
- alternative products:Isoforms differ in the C-terminal region which is encoded by alternative exons,disease:Defects in GFAP are a cause of Alexander disease (ALEXD) [MIM:203450]. Alexander disease is a rare disorder of the central nervous system. It is a progressive leukoencephalopathy whose hallmark is the widespread accumulation of Rosenthal fibers which are cytoplasmic inclusions in astrocytes. The most common form affects infants and young children, and is characterized by progressive failure of central myelination, usually leading to death usually within the first decade. Infants with Alexander disease develop a leukoencephalopathy with macrocephaly, seizures, and psychomotor retardation. Patients with juvenile or adult forms typically experience ataxia, bulbar signs and spasticity, and a more slowly progressive course.,function:GFAP, a class-III intermediate filament, is a cell-spe
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm
- Expression:
- Expressed in cells lacking fibronectin.
Crocin alleviates cognitive impairment associated with atherosclerosis via improving neuroinflammation in LDLR−/− mice fed a high-fat/cholesterol diet 2022 Jan 27. WB Mouse 1:1000 hippocampus,parietal cortex
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
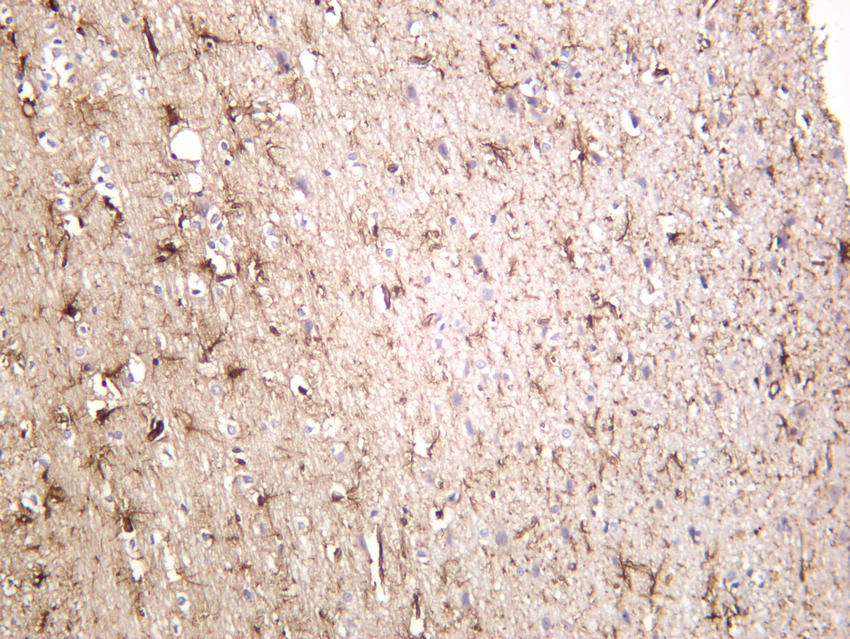
- Rat brain was stained with anti-GFAP (PT0298R) rabbit antibody
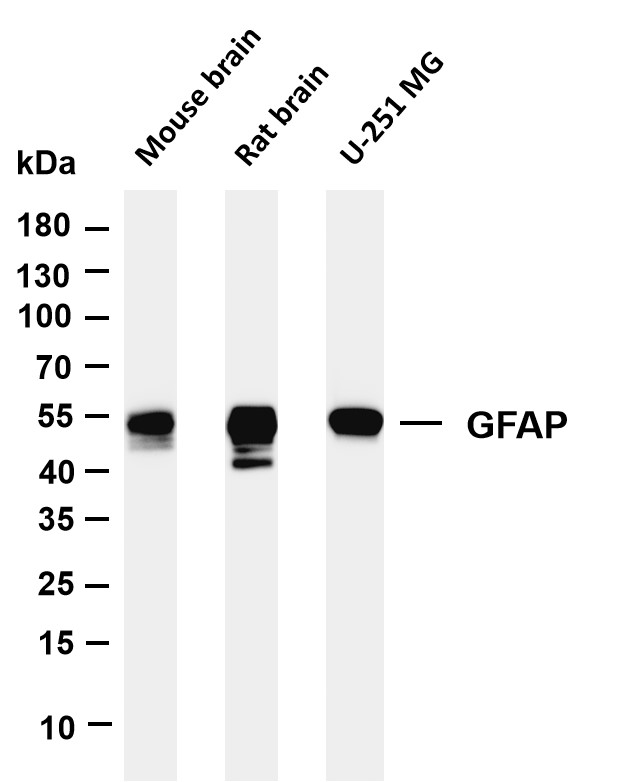
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-20% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-GFAP (PT0298R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: Mouse brain Lane 2: Rat brain Lane 3: U-251MG Predicted band size: 50kDa Observed band size: 50kDa
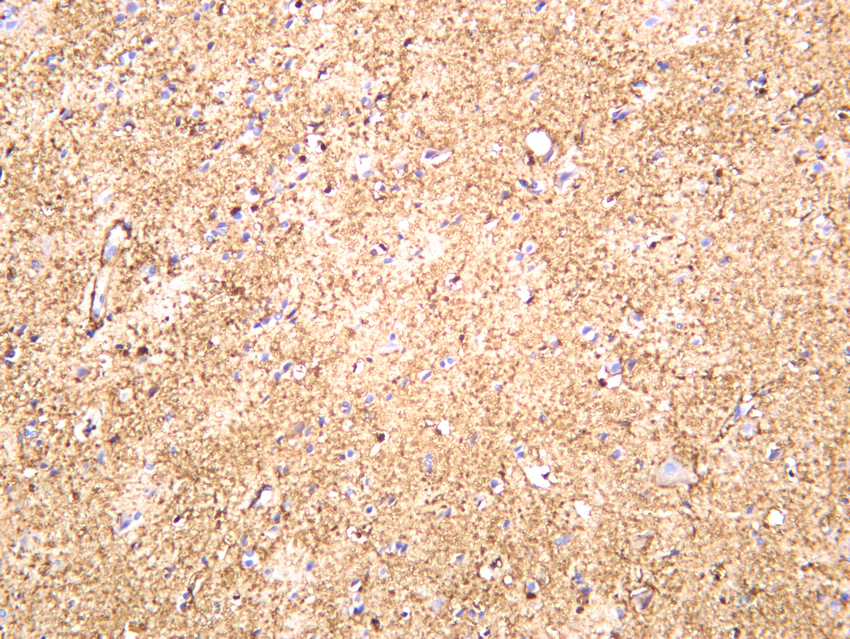
- Human brain was stained with anti-GFAP (PT0298R) rabbit antibody
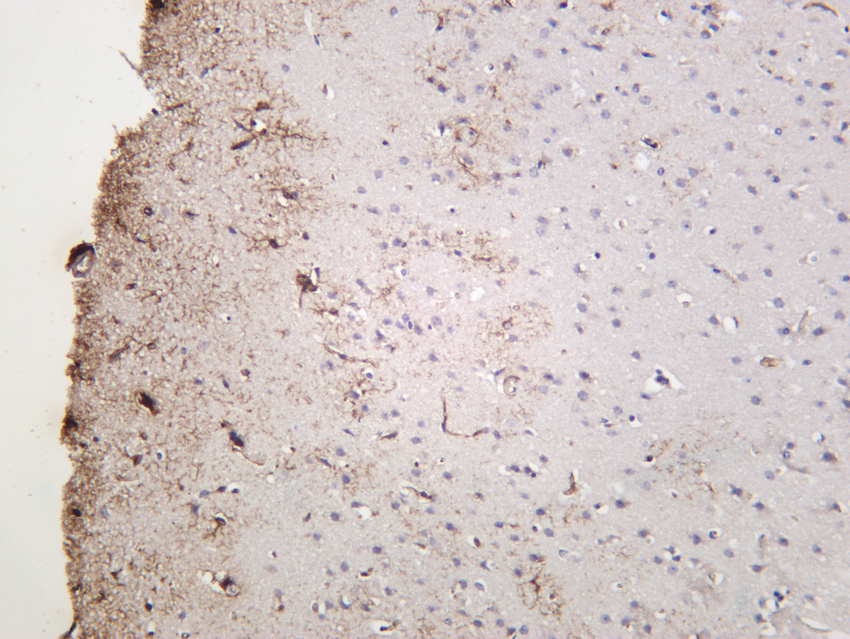
- Mouse brain was stained with anti-GFAP (PT0298R) rabbit antibody
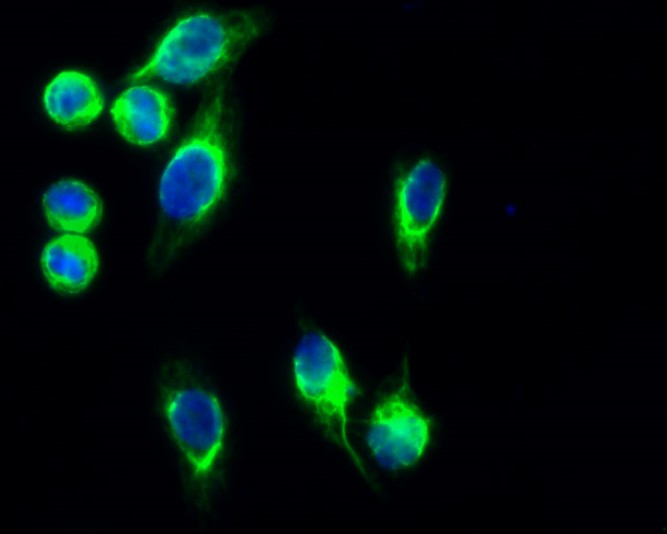
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Hela cell. 1,GFAP Antibody(green) was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Goat Anti Rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 Catalog:RS3211 was diluted at 1:1000(room temperature, 50min). 3 DAPI(blue) 10min.



