Cystatin C mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM1373
- Applications:sELISA;Capture
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Cystatin C
- Fields:
- >>Salivary secretion
- Gene Name:
- cyc
- Human Gene Id:
- 1471
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P01034
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P21460
- Immunogen:
- Recombinant human cystatin c protein.
- Specificity:
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- ELISA 1:10000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CST3;Cystatin 3.
- Observed Band(KD):
- 13kD
- Background:
- The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and the kininogens. The type 2 cystatin proteins are a class of cysteine proteinase inhibitors found in a variety of human fluids and secretions, where they appear to provide protective functions. The cystatin locus on chromosome 20 contains the majority of the type 2 cystatin genes and pseudogenes. This gene is located in the cystatin locus and encodes the most abundant extracellular inhibitor of cysteine proteases, which is found in high concentrations in biological fluids and is expressed in virtually all organs of the body. A mutation in this gene has been associate
- Function:
- disease:Defects in CST3 are the cause of amyloidosis type 6 (AMYL6) [MIM:105150]; also known as hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis (HCHWA), cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) or cerebroarterial amyloidosis Icelandic type. AMYL6 is a hereditary generalized amyloidosis due to cystatin C amyloid deposition. Cystatin C amyloid accumulates in the walls of arteries, arterioles, and sometimes capillaries and veins of the brain, and in various organs including lymphoid tissue, spleen, salivary glands, and seminal vesicles. Amyloid deposition in the cerebral vessels results in cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cerebral hemorrage and premature stroke. Cystatin C levels in the cerebrospinal fluid are abnormally low.,disease:Genetic variations in CST3 are associated with age-related macular degeneration type 11 (ARMD11) [MIM:611953]. ARMD is a multifactorial eye disease and the most common ca
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted .
- Expression:
- Expressed in submandibular and sublingual saliva but not in parotid saliva (at protein level). Expressed in various body fluids, such as the cerebrospinal fluid and plasma. Expressed in highest levels in the epididymis, vas deferens, brain, thymus, and ovary and the lowest in the submandibular gland.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
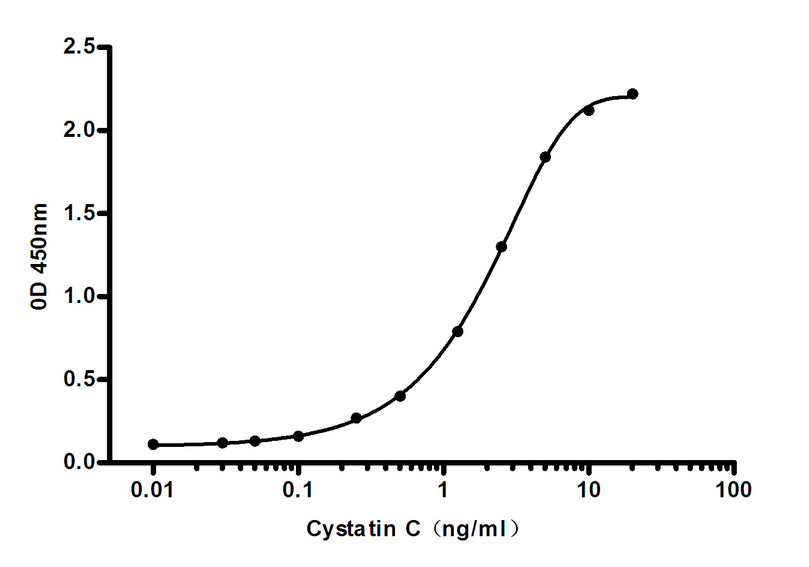
- Standard Curve for Human Cystatin C: Capture Antibody Mouse mAb [6F12-C7-D8] to Human Cystatin C at 4μg/ml and Detector Antibody Mouse mAb [7F6-A5-F3]to Human Cystatin C at 0.5μg/ml.



