c-Rel Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0164
- Applications:WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- c-Rel
- Fields:
- >>Ras signaling pathway;>>Transcriptional misregulation in cancer;>>Viral carcinogenesis
- Gene Name:
- REL
- Protein Name:
- Proto-oncogene c-Rel
- Human Gene Id:
- 5966
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q04864
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P15307
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human c-Rel expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- c-Rel Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of c-Rel protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
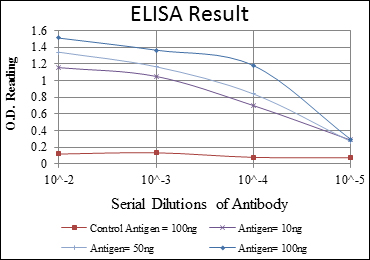
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- REL;Proto-oncogene c-Rel
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 69kD
- References:
- 1. Gut. 2009 Aug;58(8):1078-83.
2. Gene Expr. 2008;14(4):195-205.
- Background:
- This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the Rel homology domain/immunoglobulin-like fold, plexin, transcription factor (RHD/IPT) family. Members of this family regulate genes involved in apoptosis, inflammation, the immune response, and oncogenic processes. This proto-oncogene plays a role in the survival and proliferation of B lymphocytes. Mutation or amplification of this gene is associated with B-cell lymphomas, including Hodgkin's lymphoma. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene are associated with susceptibility to ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014],
- Function:
- function:Proto-oncogene that may play a role in differentiation and lymphopoiesis. NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as b
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus .
- Expression:
- Colon,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
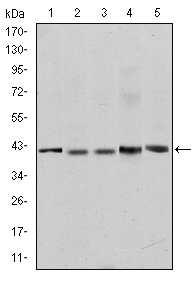
- Western Blot analysis using c-Rel Monoclonal Antibody against Jurkat (1), NIH/3T3 (2), HeLa (3), HEK293 (4) and RAJI (5) cell lysate.
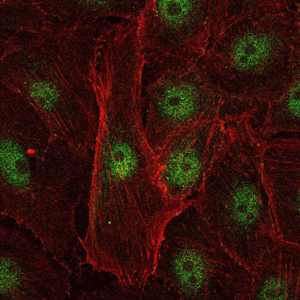
- Immunofluorescence analysis of U251 cells using c-Rel Monoclonal Antibody (green). Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye. Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin.