UDG Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4815
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- UDG
- Fields:
- >>Base excision repair;>>Primary immunodeficiency
- Gene Name:
- UNG
- Protein Name:
- Uracil-DNA glycosylase
- Human Gene Id:
- 7374
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P13051
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22256
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P97931
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human UNG. AA range:191-240
- Specificity:
- UDG Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of UDG protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:40000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- UNG;DGU;UNG1;UNG15;Uracil-DNA glycosylase;UDG
- Observed Band(KD):
- 35kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes one of several uracil-DNA glycosylases. One important function of uracil-DNA glycosylases is to prevent mutagenesis by eliminating uracil from DNA molecules by cleaving the N-glycosylic bond and initiating the base-excision repair (BER) pathway. Uracil bases occur from cytosine deamination or misincorporation of dUMP residues. Alternative promoter usage and splicing of this gene leads to two different isoforms: the mitochondrial UNG1 and the nuclear UNG2. The UNG2 term was used as a previous symbol for the CCNO gene (GeneID 10309), which has been confused with this gene, in the literature and some databases. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in UNG are a cause of immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM type 5 syndrome (HIGM5) [MIM:608106]. Hyper-IgM syndrome is a condition characterized by normal or increased serum IgM concentrations associated with low or absent serum IgG, IgA, and IgE concentrations. HIGM5 is associated with profound impairment in immunoglobulin (Ig) class-switch recombination (CSR) at a DNA precleavage step.,function:Excises uracil residues from the DNA which can arise as a result of misincorporation of dUMP residues by DNA polymerase or due to deamination of cytosine.,online information:UNG mutation db,PTM:Isoform 1 is processed by cleavage of a transit peptide.,similarity:Belongs to the uracil-DNA glycosylase family.,subunit:Monomer. Interacts with HIV-1 Vpr.,tissue specificity:Isoform 1 is widely expressed with the highest expression in skeletal muscle, heart and testicles. Isoform 2 has the hi
- Subcellular Location:
- [Isoform 1]: Mitochondrion.; [Isoform 2]: Nucleus.
- Expression:
- Isoform 1 is widely expressed with the highest expression in skeletal muscle, heart and testicles. Isoform 2 has the highest expression levels in tissues containing proliferating cells.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
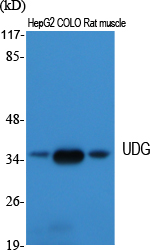
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using UDG Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of COLO205 cells using UDG Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
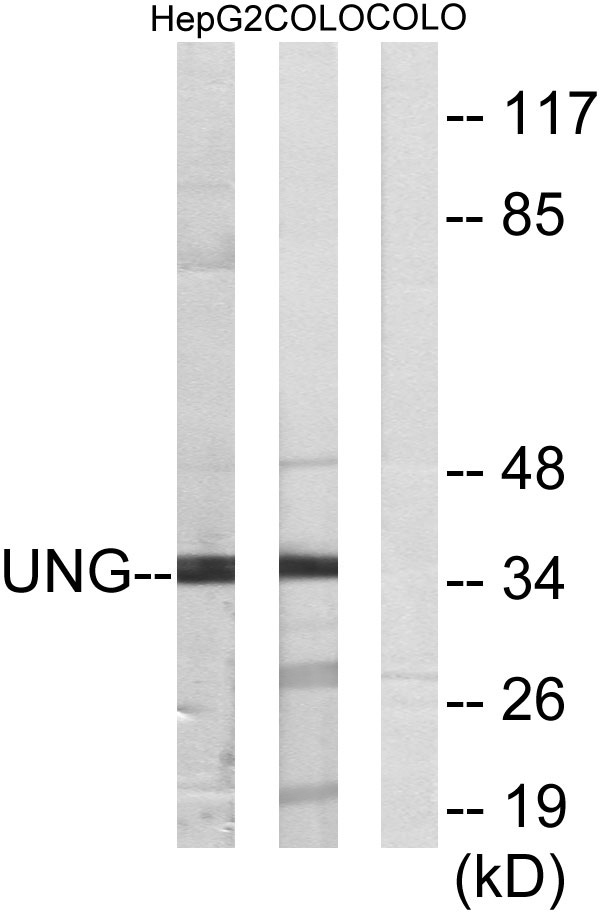
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2 and COLO cells, using UNG Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
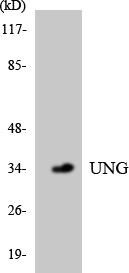
- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HepG2 cells using UNG antibody.
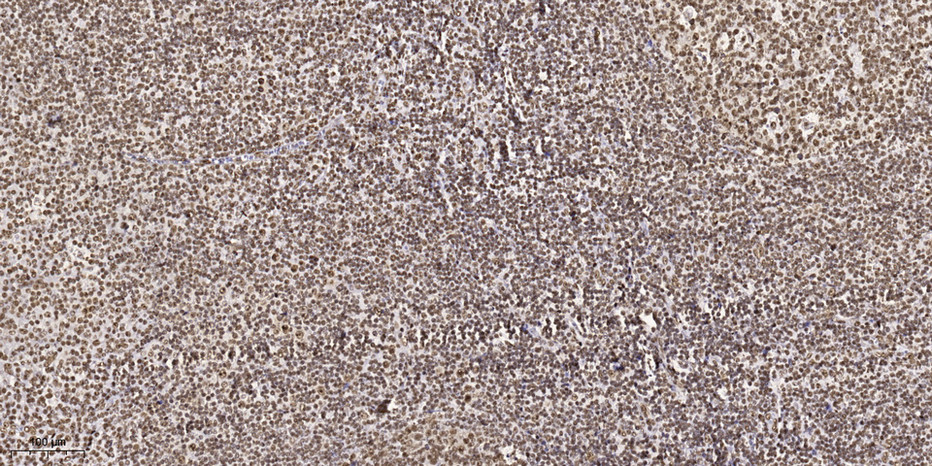
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. 1, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 2 Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight.3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



