Synuclein-β Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4498
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Synuclein-β
- Gene Name:
- SNCB
- Protein Name:
- Beta-synuclein
- Human Gene Id:
- 6620
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q16143
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 104069
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q91ZZ3
- Rat Gene Id:
- 113893
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q63754
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Synuclein beta. AA range:85-134
- Specificity:
- Synuclein-β Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Synuclein-β protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SNCB;Beta-synuclein
- Observed Band(KD):
- 14kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of a small family of proteins that inhibit phospholipase D2 and may function in neuronal plasticity. The encoded protein is abundant in lesions of patients with Alzheimer disease. A mutation in this gene was found in individuals with dementia with Lewy bodies. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015],
- Function:
- disease:Brain iron accumulation type 1 (NBIA1, also called Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome), a rare neuroaxonal dystrophy, is histologically characterized by axonal spheroids, iron deposition, Lewy body (LB)-like intraneuronal inclusions, glial inclusions and neurofibrillary tangles. SNCB is found in spheroids but not in inclusions.,function:Non-amyloid component of senile plaques found in Alzheimer disease. Could act as a regulator of SNCA aggregation process. Protects neurons from staurosporine and 6-hydroxy dopamine (6OHDA)-stimulated caspase activation in a TP53/p53-dependent manner. Contributes to restore the SNCA anti-apoptotic function abolished by 6OHDA. Not found in the Lewy bodies associated with Parkinson disease.,PTM:Phosphorylated. Phosphorylation by G-protein coupled receptor kinases (GRK) is more efficient than phosphorylation by CK1, CK2 and CaM-kinase II.,similarity:Belongs
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm.
- Expression:
- Expressed predominantly in brain; concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Synuclein-β Polyclonal Antibody
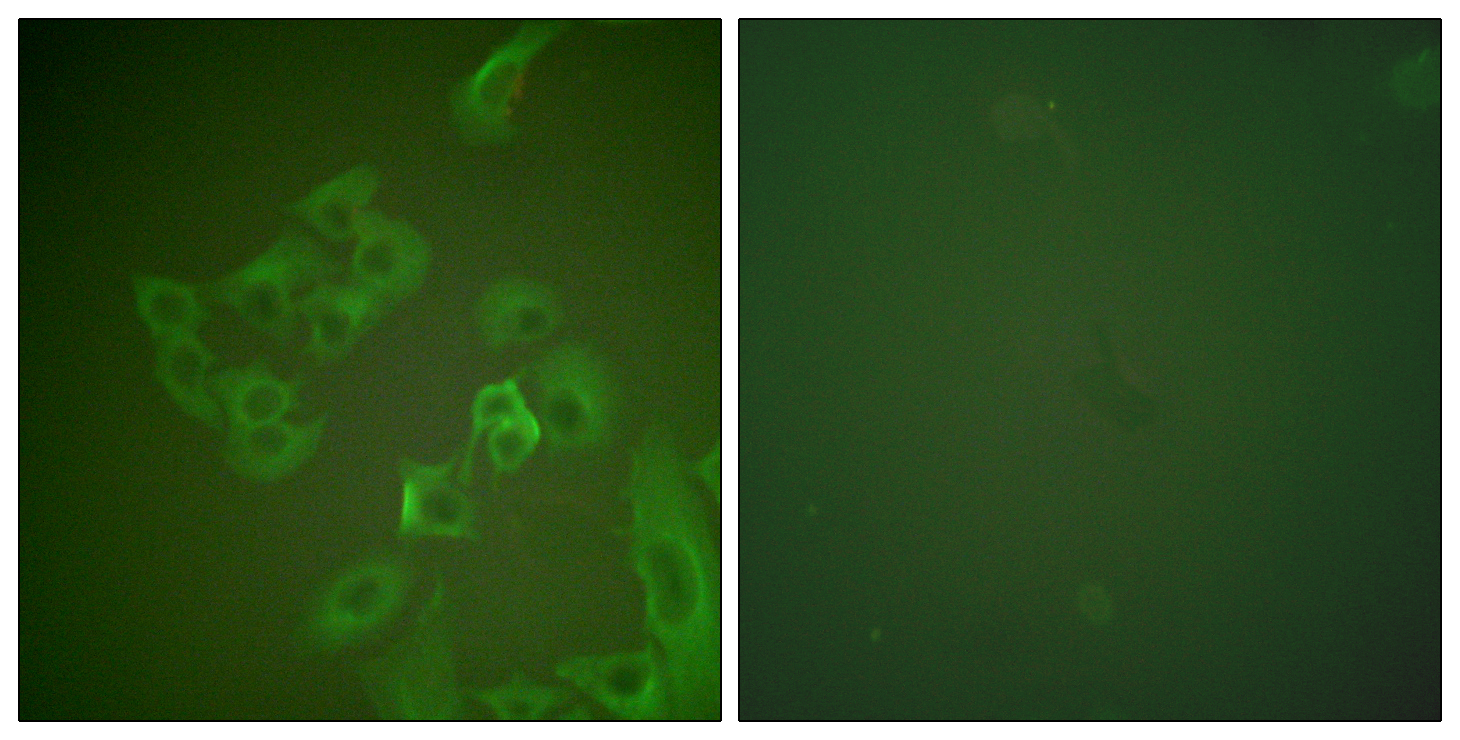
- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using Synuclein beta Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
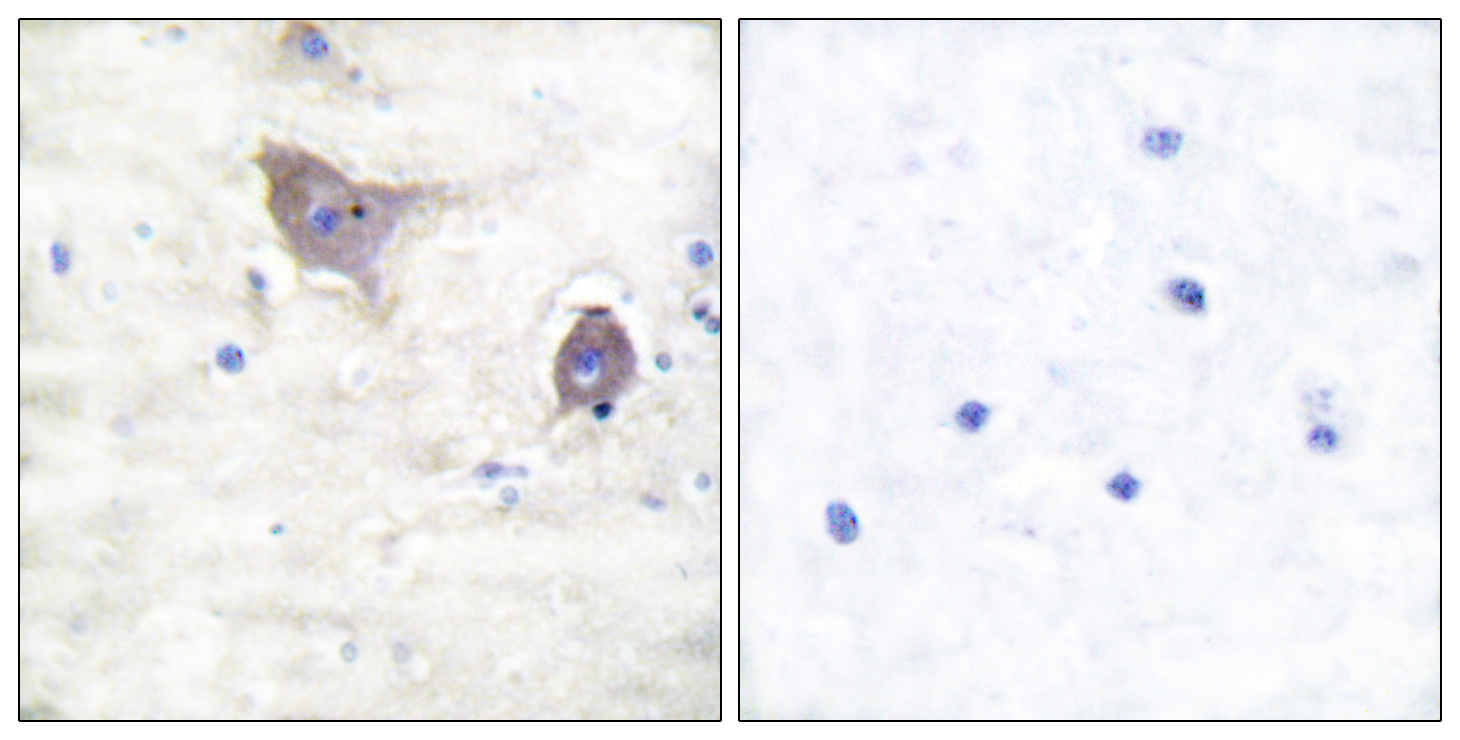
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using Synuclein beta Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
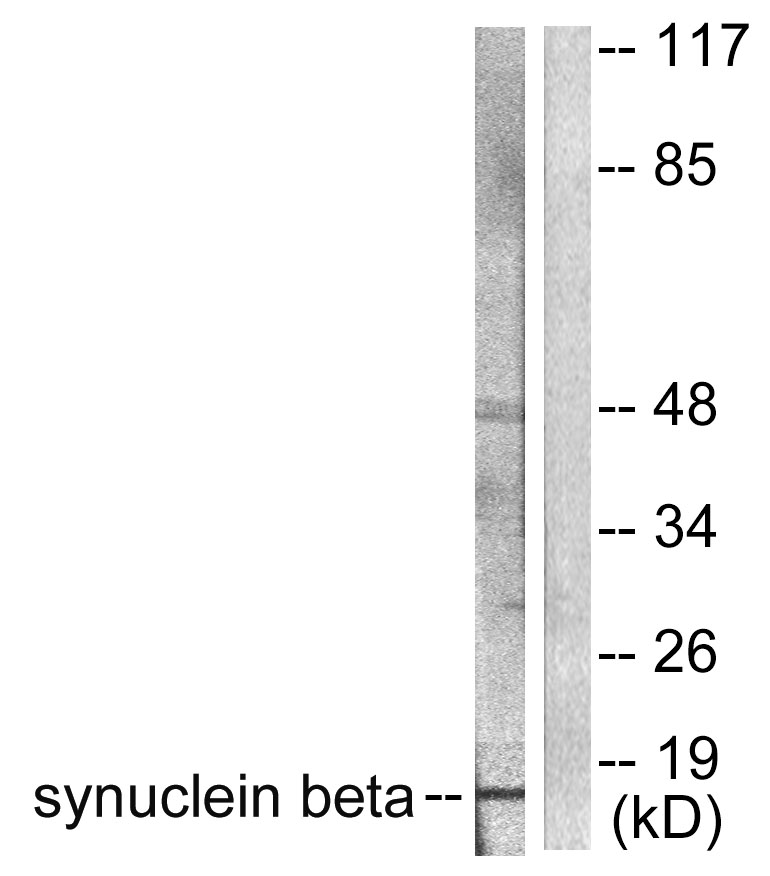
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa cells, using Synuclein beta Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.


