ROM-K Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4164
- Applications:WB;IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- ROM-K
- Fields:
- >>Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption;>>Gastric acid secretion
- Gene Name:
- KCNJ1
- Protein Name:
- ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 3758
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P48048
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 56379
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O88335
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24521
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P35560
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human ROMK/Kir1.1. AA range:11-60
- Specificity:
- ROM-K Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of ROM-K protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:50-300
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- KCNJ1;ROMK1;ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 1;ATP-regulated potassium channel ROM-K;Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir1.1;Potassium channel; inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 45kD
- Background:
- Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. It is activated by internal ATP and probably plays an important role in potassium homeostasis. The encoded protein has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell. Mutations in this gene have been associated with antenatal Bartter syndrome, which is characterized by salt wasting, hypokalemic alkalosis, hypercalciuria, and low blood pressure. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in KCNJ1 are the cause of Bartter syndrome type 2 (BS2) [MIM:241200]; also termed hyperprostanglandin E syndrome 2. BS refers to a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired salt reabsorption in the thick ascending loop of Henle with pronounced salt wasting, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, and varying degrees of hypercalciuria. BS2 is a life-threatening condition beginning in utero, with marked fetal polyuria that leads to polyhydramnios and premature delivery. Another hallmark of BS2 is a marked hypercalciuria and, as a secondary consequence, the development of nephrocalcinosis and osteopenia.,function:In the kidney, probably plays a major role in potassium homeostasis. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Phosphorylation at Ser-44 by SGK1 is necessary for its expression at the cell membrane. .
- Expression:
- In the kidney and pancreatic islets. Lower levels in skeletal muscle, pancreas, spleen, brain, heart and liver.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
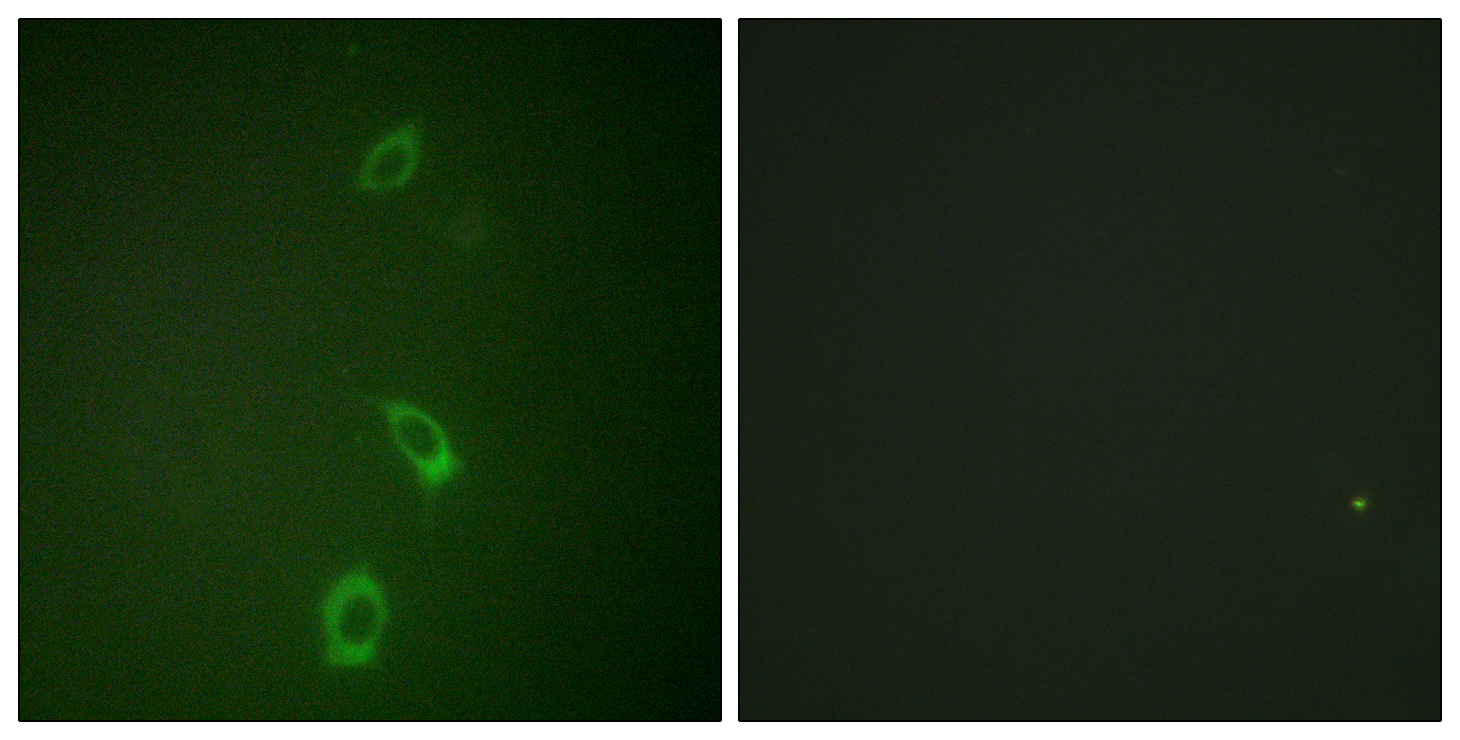
- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using ROMK/Kir1.1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.

- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human Gastric adenocarcinoma. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



