RARβ Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4008
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- RARβ
- Fields:
- >>Pathways in cancer;>>Small cell lung cancer;>>Non-small cell lung cancer;>>Gastric cancer
- Gene Name:
- RARB
- Protein Name:
- Retinoic acid receptor beta
- Human Gene Id:
- 5915
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P10826
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 218772
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P22605
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Retinoic Acid Receptor beta. AA range:331-380
- Specificity:
- RARβ Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of RARβ protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- RARB;HAP;NR1B2;Retinoic acid receptor beta;RAR-beta;HBV-activated protein;Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 2;RAR-epsilon
- Observed Band(KD):
- 50kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes retinoic acid receptor beta, a member of the thyroid-steroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear transcriptional regulators. This receptor localizes to the cytoplasm and to subnuclear compartments. It binds retinoic acid, the biologically active form of vitamin A which mediates cellular signalling in embryonic morphogenesis, cell growth and differentiation. It is thought that this protein limits growth of many cell types by regulating gene expression. The gene was first identified in a hepatocellular carcinoma where it flanks a hepatitis B virus integration site. Alternate promoter usage and differential splicing result in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014],
- Function:
- domain:Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal steroid-binding domain.,function:This is a receptor for retinoic acid. This metabolite has profound effects on vertebrate development. Retinoic acid is a morphogen and is a powerful teratogen. This receptor controls cell function by directly regulating gene expression.,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family.,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Cytoplasm .; [Isoform Beta-1]: Nucleus.; [Isoform Beta-2]: Nucleus.; [Isoform Beta-4]: Cytoplasm.
- Expression:
- Expressed in aortic endothelial cells (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
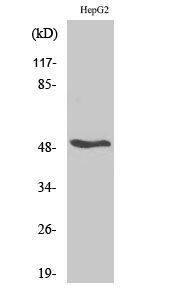
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using RARβ Polyclonal Antibody

- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue, using Retinoic Acid Receptor beta Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.

- Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2 cells, using Retinoic Acid Receptor beta Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
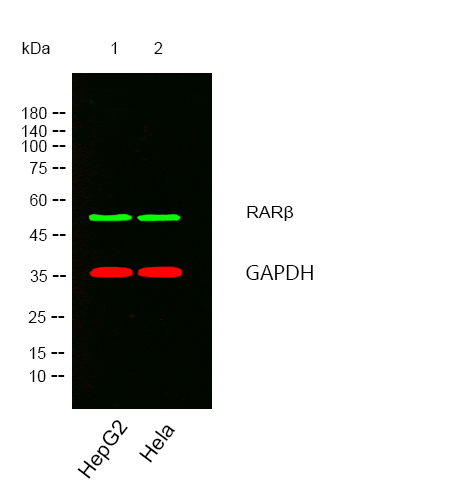
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2,Hela cells, (Green) primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night, secondary antibody was diluted at 1:10000, 37° 1hour. (Red) loading contrl antibody was diluted at 1:5000 as loading control, 4° over night,secondary antibody was diluted at 1:10000, 37° 1hour.


