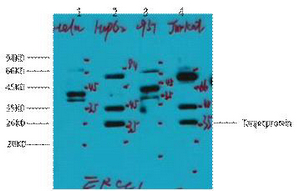
STING (Phospho Ser366) rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YP1684
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- STING/TMEM173
- Fields:
- >>NOD-like receptor signaling pathway;>>RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway;>>Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway;>>Shigellosis;>>Human cytomegalovirus infection;>>Herpes simplex virus 1 infection;>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection;>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19
- Gene Name:
- TMEM173 ERIS MITA STING
- Protein Name:
- STING (Phospho-Ser366)
- Human Gene Id:
- 340061
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q86WV6
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 72512
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q3TBT3
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human STING (Phospho-Ser366)
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of STING (Phospho-Ser366) at Human, Mouse,Rat
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Transmembrane protein 173 (Endoplasmic reticulum interferon stimulator) (ERIS) (Mediator of IRF3 activation) (hMITA) (Stimulator of interferon genes protein) (hSTING)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 38kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a five transmembrane protein that functions as a major regulator of the innate immune response to viral and bacterial infections. The encoded protein is a pattern recognition receptor that detects cytosolic nucleic acids and transmits signals that activate type I interferon responses. The encoded protein has also been shown to play a role in apoptotic signaling by associating with type II major histocompatibility complex. Mutations in this gene are the cause of infantile-onset STING-associated vasculopathy. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014],
- Function:
- function:Acts as a facilitator of innate immune signaling. Able to activate both NF-kappa-B and IRF3 transcription pathways to induce expression of type I interferon (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) and exert a potent anti-viral state following expression. May be involved in translocon function, the translocon possibly being able to influence the induction of type I interferons. May be involved in transduction of apoptotic signals via its association with the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II). Mediates death signaling via activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway.,PTM:Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues upon MHC-II aggregation.,subunit:Associates with the MHC-II complex (By similarity). Interacts with DDX58/RIG-I, MAVS/VISA and SSR2.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitously expressed.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cytoplasm, perinuclear region . Endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Golgi apparatus membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Mitochondrion outer membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . In response to double-stranded DNA stimulation, translocates from the endoplasmic reticulum through the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment and Golgi to post-Golgi vesicles, where the kinase TBK1 is recruited (PubMed:19433799, PubMed:30842659, PubMed:30842653, PubMed:29694889). Upon cGAMP-binding, translocates to the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi interme
- Expression:
- Ubiquitously expressed. Expressed in skin endothelial cells, alveolar type 2 pneumocytes, bronchial epithelium and alveolar macrophages.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs