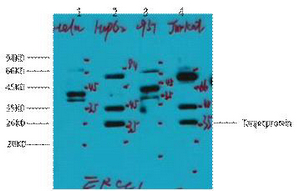
VR1 (Phospho Ser502) rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YP1679
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- VR1
- Fields:
- >>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction;>>Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels
- Gene Name:
- TRPV1 VR1
- Protein Name:
- VR1 (Phospho-Ser502)
- Human Gene Id:
- 7442
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8NER1
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 193034
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q704Y3
- Rat Gene Id:
- 83810
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- O35433
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human VR1 (Phospho-Ser502)
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of VR1 (Phospho-Ser502) at Human, Mouse,Rat
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TrpV1) (Capsaicin receptor) (Osm-9-like TRP channel 1) (OTRPC1) (Vanilloid receptor 1)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 92kD
- Background:
- transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1(TRPV1) Homo sapiens Capsaicin, the main pungent ingredient in hot chili peppers, elicits a sensation of burning pain by selectively activating sensory neurons that convey information about noxious stimuli to the central nervous system. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for capsaicin and is a non-selective cation channel that is structurally related to members of the TRP family of ion channels. This receptor is also activated by increases in temperature in the noxious range, suggesting that it functions as a transducer of painful thermal stimuli in vivo. Four transcript variants encoding the same protein, but with different 5' UTR sequence, have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:The association domain (AD) is necessary for self-association.,enzyme regulation:Channel activity is activated via the interaction with PIRT and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). Both PIRT and PIP2 are required to activate channel activity.,function:Receptor-activated non-selective calcium permeant cation channel involved in detection of noxious chemical and thermal stimuli. Seems to mediate proton influx and may be involved in intracellular acidosis in nociceptive neurons. May be involved in mediation of inflammatory pain and hyperalgesia. Sensitized by a phosphatidylinositol second messenger system activated by receptor tyrosine kinases, which involves PKC isozymes and PCL.,miscellaneous:Responses evoked by low pH and heat, and capsaicin can be antagonized by capsazepine.,PTM:Phosphorylation by PKA reverses capsaicin-induced dephosphorylation at multiple sites, proba
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell projection, dendritic spine membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Mostly, but not exclusively expressed in postsynaptic dendritic spines. .
- Expression:
- Widely expressed at low levels. Expression is elevated in dorsal root ganglia. In skin, expressed in cutaneous sensory nerve fibers, mast cells, epidermal keratinocytes, dermal blood vessels, the inner root sheet and the infundibulum of hair follicles, differentiated sebocytes, sweat gland ducts, and the secretory portion of eccrine sweat glands (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs