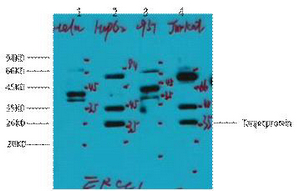
p300 (Phospho Ser1834) rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YP1674
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- p300
- Fields:
- >>Viral life cycle - HIV-1;>>cAMP signaling pathway;>>HIF-1 signaling pathway;>>FoxO signaling pathway;>>Cell cycle;>>Wnt signaling pathway;>>Notch signaling pathway;>>TGF-beta signaling pathway;>>Adherens junction;>>JAK-STAT signaling pathway;>>Long-term potentiation;>>Melanogenesis;>>Thyroid hormone signaling pathway;>>Glucagon signaling pathway;>>Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action;>>Huntington disease;>>Tuberculosis;>>Hepatitis B;>>Influenza A;>>Human papillomavirus infection;>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection;>>Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Viral carcinogenesis;>>MicroRNAs in cancer;>>Renal cell carcinoma;>>Prostate cancer
- Gene Name:
- EP300 P300
- Protein Name:
- p300 (Phospho-Ser1834)
- Human Gene Id:
- 2033
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q09472
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- B2RWS6
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human p300 (Phospho-Ser1834)
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of p300 (Phospho-Ser1834) at Human, Mouse,Rat
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Histone acetyltransferase p300 (p300 HAT) (EC 2.3.1.48) (E1A-associated protein p300)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 266kD
- Background:
- E1A binding protein p300(EP300) Homo sapiens This gene encodes the adenovirus E1A-associated cellular p300 transcriptional co-activator protein. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription via chromatin remodeling and is important in the processes of cell proliferation and differentiation. It mediates cAMP-gene regulation by binding specifically to phosphorylated CREB protein. This gene has also been identified as a co-activator of HIF1A (hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha), and thus plays a role in the stimulation of hypoxia-induced genes such as VEGF. Defects in this gene are a cause of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and may also play a role in epithelial cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:Acetyl-CoA + histone = CoA + acetylhistone.,disease:Chromosomal aberrations involving EP300 may be a cause of acute myeloid leukemias. Translocation t(8;22)(p11;q13) with MYST3.,disease:Defects in EP300 are a cause of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) [MIM:180849]. RSTS is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by craniofacial abnormalities, broad thumbs, broad big toes, mental retardation and a propensity for development of malignancies.,disease:Defects in EP300 may play a role in epithelial cancer.,function:Functions as histone acetyltransferase and regulates transcription via chromatin remodeling. Acetylates all four core histones in nucleosomes. Histone acetylation gives an epigenetic tag for transcriptional activation. Binds to and may be involved in the transforming capacity of the adenovirus E1A protein. Mediates cAMP-gene regulation by binding specifically
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Chromosome . Localizes to active chromatin: Colocalizes with histone H3 acetylated and/or crotonylated at 'Lys-18' (H3K18ac and H3K18cr, respectively) (PubMed:25818647). In the presence of ALX1 relocalizes from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Colocalizes with ROCK2 in the nucleus (PubMed:12929931). .
- Expression:
- Epithelium,Skin,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs