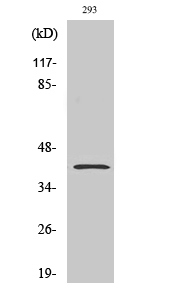
PAR4 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0504
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- PAR4
- Gene Name:
- PAWR
- Protein Name:
- PRKC apoptosis WT1 regulator protein
- Human Gene Id:
- 5074
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q96IZ0
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q925B0
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of PAR4 (aa1-330) expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- PAR4 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PAR4 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PAWR;PAR4;PRKC apoptosis WT1 regulator protein;Prostate apoptosis response 4 protein;Par-4
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 37kD
- References:
- 1. J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 2;279(27):28266-75.
2. Exp Hematol. 2004 Jul;32(7):649-56.
3. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(3):1146-61.
4. Psychiatr Genet. 2006 Oct;16(5):193-6.
- Background:
- The tumor suppressor WT1 represses and activates transcription. The protein encoded by this gene is a WT1-interacting protein that itself functions as a transcriptional repressor. It contains a putative leucine zipper domain which interacts with the zinc finger DNA binding domain of WT1. This protein is specifically upregulated during apoptosis of prostate cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:The leucine-zipper domain is not essential for apoptosis, but is required for sensitization of cells to exogenous apoptotic insults and for interaction with its partners.,domain:The SAC domain is a death-inducing domain selective for apoptosis induction in cancer cells. This domain is essential for nuclear entry, Fas activation, inhibition of NF-kappa-B activity and induction of apoptosis in cancer cells.,function:Pro-apoptopic protein capable of selectively inducing apoptosis in cancer cells, sensitizing the cells to diverse apoptotic stimuli and causing regression of tumors in animal models. Induces apoptosis in certain cancer cells by activation of the Fas prodeath pathway and coparallel inhibition of NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity. Inhibits the transcriptional activation and augments the transcriptional repression mediated by WT1. Down-regulates the anti-apoptotic protein
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Mainly cytoplasmic in absence of apoptosis signal and in normal cells. Nuclear in most cancer cell lines. Nuclear entry seems to be essential but not sufficient for apoptosis (By similarity). Nuclear localization includes nucleoplasm and PML nuclear bodies. .
- Expression:
- Widely expressed. Expression is elevated in various neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer, Parkinson and Huntington diseases and stroke. Down-regulated in several cancers.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
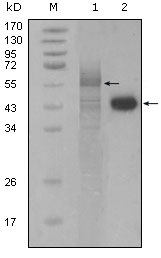
- Western Blot analysis using PAR4 Monoclonal Antibody against full-length Trx-PAR4 recombinant protein (1) and HeLa cell lysate (2).
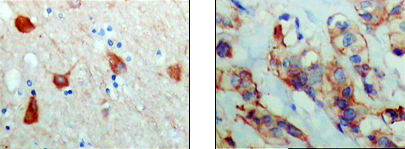
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain (left) and breast carcinoma (right), showing cytoplasmic and membrane localization with DAB staining using PAR4 Monoclonal Antibody.