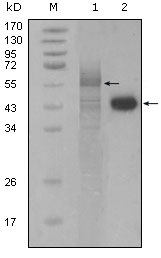
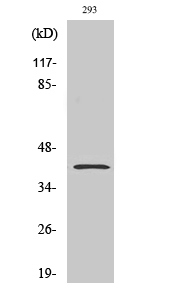
Total PAR4 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3364C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- PAWR
- Human Gene Id:
- 5074
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q96IZ0
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q925B0
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q62627
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- PRKC apoptosis WT1 regulator protein (Prostate apoptosis response 4 protein) (Par-4)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- domain:The leucine-zipper domain is not essential for apoptosis, but is required for sensitization of cells to exogenous apoptotic insults and for interaction with its partners.,domain:The SAC domain is a death-inducing domain selective for apoptosis induction in cancer cells. This domain is essential for nuclear entry, Fas activation, inhibition of NF-kappa-B activity and induction of apoptosis in cancer cells.,function:Pro-apoptopic protein capable of selectively inducing apoptosis in cancer cells, sensitizing the cells to diverse apoptotic stimuli and causing regression of tumors in animal models. Induces apoptosis in certain cancer cells by activation of the Fas prodeath pathway and coparallel inhibition of NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity. Inhibits the transcriptional activation and augments the transcriptional repression mediated by WT1. Down-regulates the anti-apoptotic protein BCL2 via its interaction with WT1. Seems also to be a transcriptional repressor by itself. May be directly involved in regulating the amyloid precursor protein (APP) cleavage activity of BACE1.,induction:By apoptosis.,PTM:Preferentially phosphorylated at the Thr-163 by PKC in cancer cells.,subcellular location:Mainly cytoplasmic in absence of apoptosis signal and in normal cells. Nuclear in most cancer cell lines. Nuclear entry seems to be essential but not sufficient for apoptosis (By similarity). Nuclear localization includes nucleoplasm and PML nuclear bodies.,subunit:Interacts with WT1, via the C-terminal region. Homooligomer. Interacts also with a wide variety of proteins, such as atypical PKCs, p62, DAPK3 kinase and THAP1. Interacts with actin, AATF, BACE1, SPSB1, SPSB2 AND SPSB4. Component of a ternary complex composed of SQSTM1 and PRKCZ.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed. Expression is elevated in various neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer, Parkinson and Huntington diseases and stroke. Down-regulated in several cancers.,
- Function:
- negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, cytokine production, negative regulation of immune system process, regulation of leukocyte activation, negative regulation of leukocyte activation, transcription,regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, apoptosis,cell death, negative regulation of cell proliferation, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, negative regulation of signal transduction, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process,positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process,negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of gene e
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Mainly cytoplasmic in absence of apoptosis signal and in normal cells. Nuclear in most cancer cell lines. Nuclear entry seems to be essential but not sufficient for apoptosis (By similarity). Nuclear localization includes nucleoplasm and PML nuclear bodies. .
- Expression:
- Widely expressed. Expression is elevated in various neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer, Parkinson and Huntington diseases and stroke. Down-regulated in several cancers.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs