T-type Ca++ CP α1H Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4773
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- T-type Ca++ CP α1H
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Calcium signaling pathway;>>Circadian entrainment;>>Aldosterone synthesis and secretion;>>Cortisol synthesis and secretion;>>GnRH secretion;>>Cushing syndrome
- Gene Name:
- CACNA1H
- Protein Name:
- Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1H
- Human Gene Id:
- 8912
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O95180
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O88427
- Rat Gene Id:
- 114862
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9EQ60
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human CACNA1H. AA range:462-511
- Specificity:
- T-type Ca++ CP α1H Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of T-type Ca++ CP α1H protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CACNA1H;Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1H;Low-voltage-activated calcium channel alpha1 3.2 subunit;Voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav3.2
- Observed Band(KD):
- 259kD
- Background:
- calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 H(CACNA1H) Homo sapiens This gene encodes a T-type member of the alpha-1 subunit family, a protein in the voltage-dependent calcium channel complex. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization and consist of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta, beta, and gamma subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. The alpha-1 subunit has 24 transmembrane segments and forms the pore through which ions pass into the cell. There are multiple isoforms of each of the proteins in the complex, either encoded by different genes or the result of alternative splicing of transcripts. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized for the gene described here. Studies suggest certain mutations in this gene lead to childhood absence epilepsy (CAE). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in CACNA1H are a cause of susceptibility to idiopathic generalized epilepsy type 6 (IGE6) [MIM:611942]. IGE is characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. IGE6 is a polygenic and multifactorial disease.,domain:Each of the four internal repeats contains five hydrophobic transmembrane segments (S1, S2, S3, S5, S6) and one positively charged transmembrane segment (S4). S4 segments probably represent the voltage-sensor and are characterized by a series of positively charged amino acids at every third position.,function:Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Interaction with STAC increases expression at the cell membrane. .
- Expression:
- Expressed in the adrenal glomerulosa (at protein level) (PubMed:25907736, PubMed:27729216). In nonneuronal tissues, the highest expression levels are found in the kidney, liver, and heart. In the brain, most abundant in the amygdala, caudate nucleus, and putamen (PubMed:9670923, PubMed:9930755). In the heart, expressed in blood vessels. ; [Isoform 1]: Expressed in testis, primarily in the germ cells, but not in other portions of the reproductive tract, such as ductus deferens (PubMed:11751928). Expressed in the brain (PubMed:11751928). ; [Isoform 2]: Expressed in testis, primarily in the germ cells, but not in other portions of the reproductive tract, such as ductus deferens (PubMed:11751928). Not expressed in the brain (PubMed:11751928).
A circuit of COCH neurons encodes social-stress-induced anxiety via MTF1 activation of Cacna1h. Cell Reports Cell Rep. 2021 Dec;37:110177 WB Mouse 1:1000 COCH neuron
CACNA1H downregulation induces skeletal muscle atrophy involving endoplasmic reticulum stress activation and autophagy flux blockade. Cell Death & Disease Cell Death Dis. 2020 Apr;11(4):1-14 WB Mouse 1:1000 Myotubes
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
.jpg)
- Li, S., Hao, M., Li, B. et al. CACNA1H downregulation induces skeletal muscle atrophy involving endoplasmic reticulum stress activation and autophagy flux blockade. Cell Death Dis 11, 279 (2020).
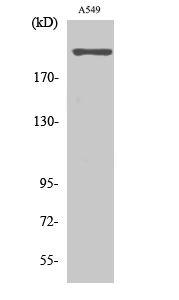
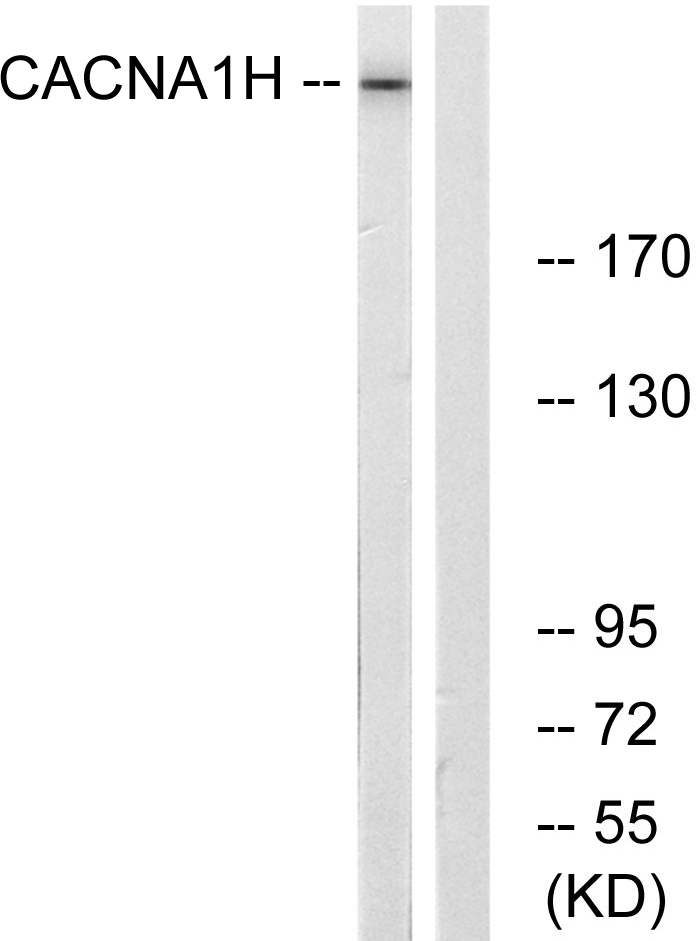
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using T-type Ca++ CP α1H Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000

- Western blot analysis of lysates from A549 cells, using CACNA1H Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
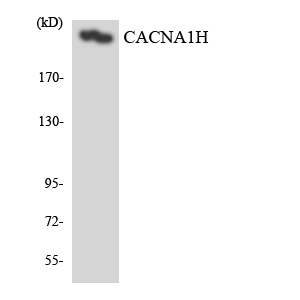
- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HeLa cells using CACNA1H antibody.


