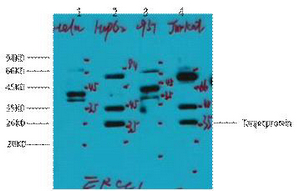
Smad4 (Phospho Thr276) rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YP1667
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Smad4
- Fields:
- >>FoxO signaling pathway;>>Cell cycle;>>Wnt signaling pathway;>>TGF-beta signaling pathway;>>Apelin signaling pathway;>>Hippo signaling pathway;>>Adherens junction;>>Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells;>>Th17 cell differentiation;>>AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications;>>Hepatitis B;>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Colorectal cancer;>>Pancreatic cancer;>>Chronic myeloid leukemia;>>Hepatocellular carcinoma;>>Gastric cancer
- Gene Name:
- SMAD4 DPC4 MADH4
- Protein Name:
- Smad4 (Phospho-Thr276)
- Human Gene Id:
- 4089
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q13485
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 17128
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P97471
- Rat Gene Id:
- 50554
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- O70437
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Smad4 (Phospho-Thr276)
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of Smad4 (Phospho-Thr276) at Human, Mouse,Rat
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 (MAD homolog 4) (Mothers against DPP homolog 4) (Deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4) (SMAD family member 4) (SMAD 4) (Smad4) (hSMAD4)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 61kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the Smad family of signal transduction proteins. Smad proteins are phosphorylated and activated by transmembrane serine-threonine receptor kinases in response to TGF-beta signaling. The product of this gene forms homomeric complexes and heteromeric complexes with other activated Smad proteins, which then accumulate in the nucleus and regulate the transcription of target genes. This protein binds to DNA and recognizes an 8-bp palindromic sequence (GTCTAGAC) called the Smad-binding element (SBE). The Smad proteins are subject to complex regulation by post-translational modifications. Mutations or deletions in this gene have been shown to result in pancreatic cancer, juvenile polyposis syndrome, and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SMAD4 are a cause of juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) [MIM:174900]; also known as juvenile intestinal polyposis (JIP). JPS is an autosomal dominant gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis syndrome in which patients are at risk for developing gastrointestinal cancers. The lesions are typified by a smooth histological appearance, predominant stroma, cystic spaces and lack of a smooth muscle core. Multiple juvenile polyps usually occur in a number of Mendelian disorders. Sometimes, these polyps occur without associated features as in JPS; here, polyps tend to occur in the large bowel and are associated with an increased risk of colon and other gastrointestinal cancers.,disease:Defects in SMAD4 are a cause of juvenile polyposis/hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia syndrome (JP/HHT) [MIM:175050]. JP/HHT syndrome phenotype consists of the coexistence of juvenile polyposis
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasmic in the absence of ligand. Migrates to the nucleus when complexed with R-SMAD (PubMed:15799969). PDPK1 prevents its nuclear translocation in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:17327236). .
- Expression:
- Fetal brain,Muscle,Placenta,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs