Wee 1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4903
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- WEE1
- Fields:
- >>Cell cycle;>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Gene Name:
- WEE1
- Protein Name:
- Wee1-like protein kinase
- Human Gene Id:
- 7465
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P30291
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22390
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P47810
- Rat Gene Id:
- 308937
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q63802
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human WEE1. AA range:19-68
- Specificity:
- Wee 1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Wee 1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:40000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- WEE1;Wee1-like protein kinase;WEE1hu;Wee1A kinase
- Observed Band(KD):
- 72kD
- Background:
- WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase(WEE1) Homo sapiens This gene encodes a nuclear protein, which is a tyrosine kinase belonging to the Ser/Thr family of protein kinases. This protein catalyzes the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of CDC2/cyclin B kinase, and appears to coordinate the transition between DNA replication and mitosis by protecting the nucleus from cytoplasmically activated CDC2 kinase. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,cofactor:Binds 2 magnesium ions per subunit.,enzyme regulation:Synthesis is increased during S and G2 phases, presumably by an increase in transcription; activity is decreased by phosphorylation during m phase. Protein levels fall in M phase as a result of decreased synthesis combined with degradation. Activity seems to be negatively regulated by phosphorylation upon entry into mitosis, although N-terminal phosphorylation might also regulate the protein stability via protection from proteolysis or might regulate the subcellular location.,function:May act as a negative regulator of entry into mitosis (G2 to M transition) by protecting the nucleus from cytoplasmically activated cyclin B1-complexed CDC2 before the onset of mitosis. Its activity increases during S and G2 phases and decreases at M phase
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus.
- Expression:
- Amygdala,Blood,Epithelium,Human uterus endothel primary cell culture,Placenta,Skin,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
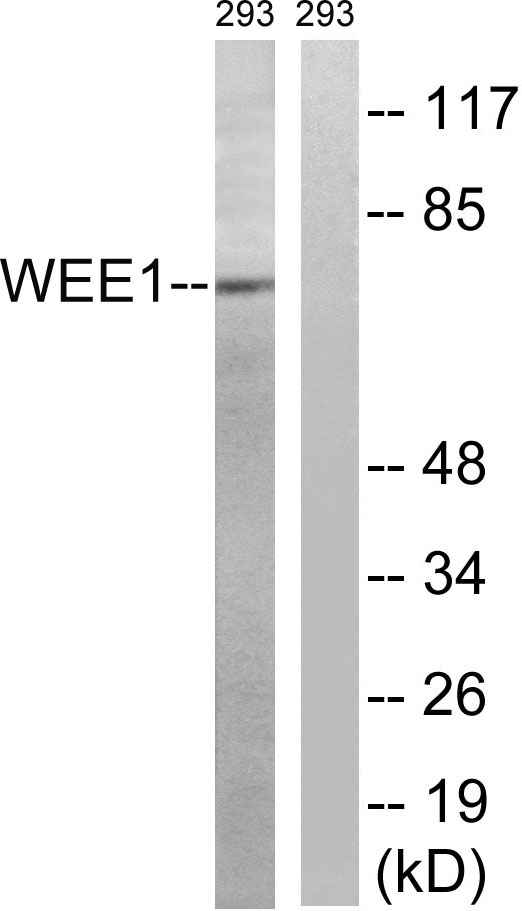
- Western blot analysis of lysates from 293 cells, using WEE1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.


