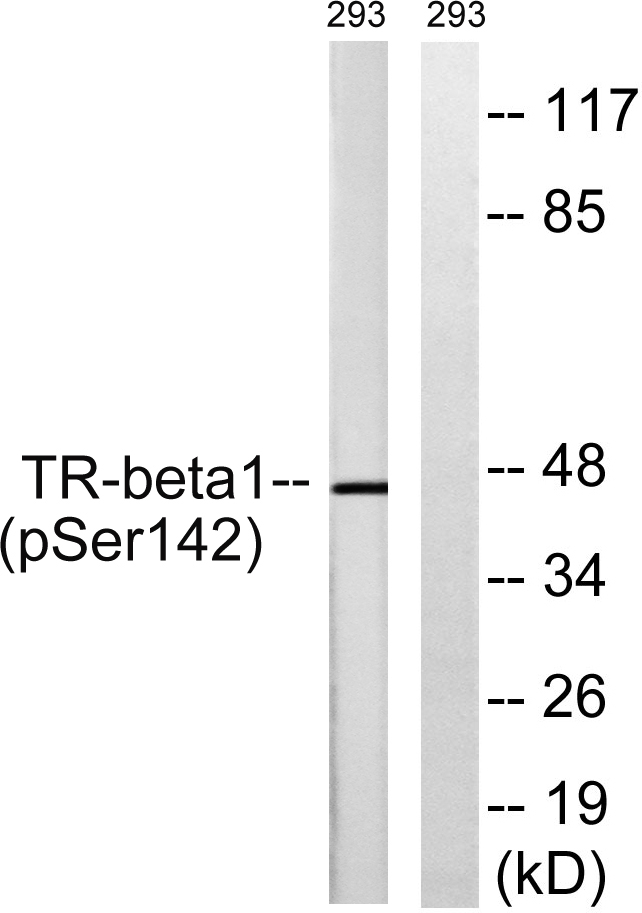
TRβ1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4756
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- TRβ1
- Fields:
- >>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction;>>Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- THRB
- Protein Name:
- Thyroid hormone receptor beta
- Human Gene Id:
- 7068
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P10828
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 21834
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P37242
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P18113
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Thyroid Hormone Receptor beta. AA range:11-60
- Specificity:
- TRβ1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of TRβ1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- THRB;ERBA2;NR1A2;THR1;Thyroid hormone receptor beta;Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group A member 2;c-erbA-2;c-erbA-beta
- Observed Band(KD):
- 53kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear hormone receptor for triiodothyronine. It is one of the several receptors for thyroid hormone, and has been shown to mediate the biological activities of thyroid hormone. Knockout studies in mice suggest that the different receptors, while having certain extent of redundancy, may mediate different functions of thyroid hormone. Mutations in this gene are known to be a cause of generalized thyroid hormone resistance (GTHR), a syndrome characterized by goiter and high levels of circulating thyroid hormone (T3-T4), with normal or slightly elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in THRB are the cause of generalized thyroid hormone resistance (GTHR) [MIM:188570, 274300]. GTHR is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait, but an autosomal recessive form also exists. The disease is characterized by goiter, abnormal mental functions, increased susceptibility to infections, abnormal growth and bone maturation, tachycardia and deafness. Affected individuals may also have attention deficit-hyperactivity disorders (ADHD) and language difficulties. GTHR patients also have high levels of circulating thyroid hormones (T3-T4), with normal or slightly elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).,disease:Defects in THRB are the cause of selective pituitary thyroid hormone resistance (PRTH) [MIM:145650]; also called familial hyperthyroidism due to inappropriate thyrotropin secretion. PRTH is a variant form of thyroid hormone resistance and is characterized by c
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus.
- Expression:
- Brain,Kidney,Pituitary,Placenta,Testis,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma tissue, using Thyroid Hormone Receptor beta Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
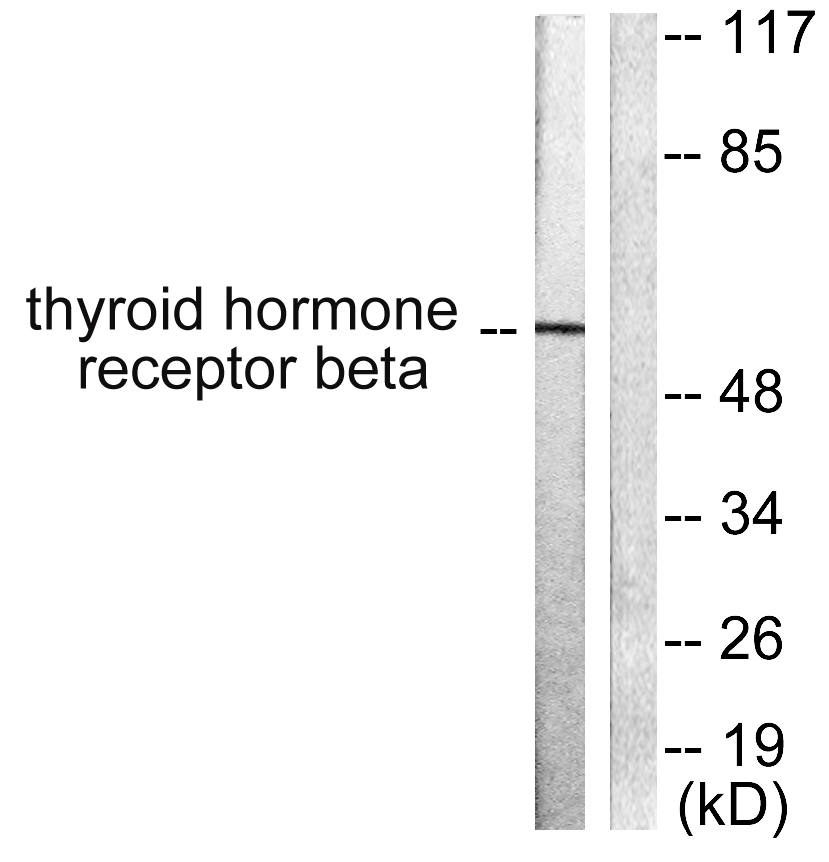
- Western blot analysis of lysates from LOVO cells, using Thyroid Hormone Receptor beta Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.