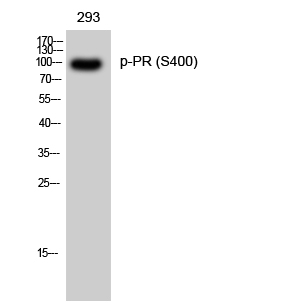
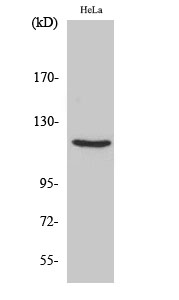
Phospho Progesterone Receptor (S400) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1328C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Gene Name:
- PGR
- Human Gene Id:
- 5241
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P06401
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q00175
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Progesterone receptor (PR) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 3)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- domain:Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal steroid-binding domain.,function:Isoform A is inactive in stimulating c-Src/MAPK signaling on hormone stimulation.,function:The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Progesterone receptor isoform B (PRB) is involved activation of c-SRC/MAPK signaling on hormone stimulation.,online information:Progesterone receptor entry,PTM:Phosphorylated on multiple serine sites. Several of these sites are hormone-dependent. Phosphorylation on Ser-294 occurs preferentially on isoform B, is highly hormone-dependent and modulates ubiquitination and sumoylation on Lys-388. Phosphorylation on Ser-102 and Ser-345 also requires induction by hormone. Basal phosphorylation on Ser-81, Ser-162, Ser-190 and Ser-400 is increased in response to progesterone and can be phosphorylated in vitro by the CDK2-A1 complex. Increased levels of phosphorylation on Ser-400 also in the presence of EGF, heregulin, IGF, PMA and FBS. Phosphorylation at this site by CDK2 is ligand-independent, and increases nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-162 and Ser-294, but not at Ser-190, is impaired during the G(2)/M phase of the cell cycle. Phosphorylation on Ser-345 by ERK1/2 MAPK is required for interaction with SP1.,PTM:Sumoylation is hormone-dependent and represses transcriptional activity. Sumoylation on all three sites is enhanced by PIAS3. Desumoylated by SENP1. Sumoylation on Lys-388, the main site of sumoylation, is repressed by ubiquitination on the same site, and modulated by phosphorylation at Ser-294.,PTM:Ubiquitination is hormone-dependent and represses sumoylation on the same site. Promoted by MAPK-mediated phosphorylation on Ser-294.,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family.,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR3 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain.,subcellular location:Mainly nuclear.,subcellular location:Nucleoplasmic shuttling is both homone- and cell cycle-dependent. On hormone stimulation, retained in the cytoplasm in the G(1) and G(2)/M phases.,subunit:Interacts with SMARD1 and UNC45A. Interacts with CUEDC2; the interaction promotes ubiquitination, decreases sumoylation, and repesses transcriptional activity. Interacts with PIAS3; the interaction promotes sumoylation of PR in a hormone-dependent manner, inhibits DNA-binding, and alters nuclear export. Interacts with SP1; the interaction requires ligand-induced phosphorylation on Ser-345 by ERK1/2 MAPK.,
- Function:
- ovulation from ovarian follicle, epithelial cell development, epithelial cell maturation, reproductive developmental process, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, intracellular signaling cascade, cell-cell signaling,gamete generation, female gamete generation, sex differentiation, gonad development, female gonad development,sexual reproduction, developmental maturation, ovulation cycle process, steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway,intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway, ovulation, epithelial cell differentiation, mammary gland development, multicellular organism reproduction, regulation of cell proliferation, ovulation cycle, development of primary sexual characteristics, regulation of transcription, development of primary female sexual characteristics,female sex differentiation, cell maturation, rhythmic process, reproductive structure development,
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Nucleoplasmic shuttling is both hormone- and cell cycle-dependent. On hormone stimulation, retained in the cytoplasm in the G(1) and G(2)/M phases.; [Isoform A]: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mainly nuclear.; [Isoform 4]: Mitochondrion outer membrane .
- Expression:
- In reproductive tissues the expression of isoform A and isoform B varies as a consequence of developmental and hormonal status. Isoform A and isoform B are expressed in comparable levels in uterine glandular epithelium during the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle. Expression of isoform B but not of isoform A persists in the glands during mid-secretory phase. In the stroma, isoform A is the predominant form throughout the cycle. Heterogeneous isoform expression between the glands of the endometrium basalis and functionalis is implying region-specific responses to hormonal stimuli.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs