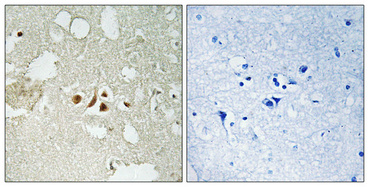
Smad2 (phospho Ser250) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0361
- Applications:WB;ELISA;IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Smad2
- Fields:
- >>Cell cycle;>>Endocytosis;>>Cellular senescence;>>TGF-beta signaling pathway;>>Apelin signaling pathway;>>Hippo signaling pathway;>>Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells;>>Th17 cell differentiation;>>Relaxin signaling pathway;>>AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications;>>Chagas disease;>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Proteoglycans in cancer;>>Colorectal cancer;>>Pancreatic cancer;>>Hepatocellular carcinoma;>>Gastric cancer;>>Inflammatory bowel disease;>>Diabetic cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- SMAD2
- Protein Name:
- Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2
- Human Gene Id:
- 4087
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q15796
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 17126
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q62432
- Rat Gene Id:
- 29357
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- O70436
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Smad2 around the phosphorylation site of Ser250. AA range:216-265
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Smad2 (S250) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Smad2 protein only when phosphorylated at S250.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:50-300; ELISA 2000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SMAD2;MADH2;MADR2;Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2;MAD homolog 2;Mothers against DPP homolog 2;JV18-1;Mad-related protein 2;hMAD-2;SMAD family member 2;SMAD 2;Smad2;hSMAD2
- Observed Band(KD):
- 65kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. This protein mediates the signal of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta, and thus regulates multiple cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. This protein is recruited to the TGF-beta receptors through its interaction with the SMAD anchor for receptor activation (SARA) protein. In response to TGF-beta signal, this protein is phosphorylated by the TGF-beta receptors. The phosphorylation induces the dissociation of this protein with SARA and the association with the family member SMAD4. The association with SMAD4 is important for the translocation
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SMAD2 are found in sporadic cases of colorectal carcinoma.,function:Transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta and activin type 1 receptor kinase. SMAD2 is a receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD). May act as a tumor suppressor in colorectal carcinoma.,PTM:Acetylated on Lys-19 by coactivators in response to TGF-beta signaling, which increases transcriptional activity. Isoform short: Acetylation increases DNA binding activity in vitro and enhances its association with target promoters in vivo.,PTM:In response to TGF-beta, ubiquitinated by NEDD4L; which promotes its degradation.,PTM:Phosphorylated on one or several of Thr-220, Ser-245, Ser-250, and Ser-255. In response to TGF-beta, phosphorylated on Ser-465/467 by TGF-beta and activin type 1 receptor kinases. Able to interact with SMURF2 when phosphorylated on Ser-465/467, recruiting other proteins, such as SNON, for degr
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasmic and nuclear in the absence of TGF-beta. On TGF-beta stimulation, migrates to the nucleus when complexed with SMAD4 (PubMed:9865696, PubMed:21145499). On dephosphorylation by phosphatase PPM1A, released from the SMAD2/SMAD4 complex, and exported out of the nucleus by interaction with RANBP1 (PubMed:16751101, PubMed:19289081). Localized mainly to the nucleus in the early stages of embryo development with expression becoming evident in the cytoplasm at the blastocyst and epiblast stages (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Expressed at high levels in skeletal muscle, endothelial cells, heart and placenta.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs