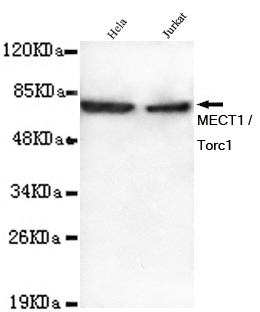
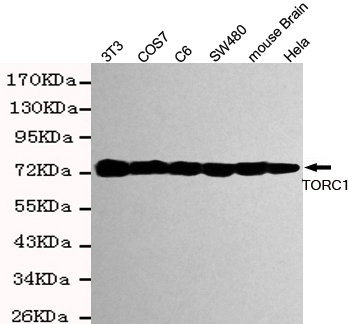
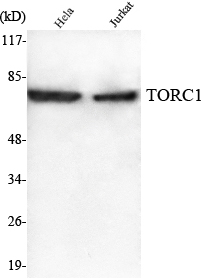
TORC1 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0624
- Applications:WB;IF;FCM;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- TORC1
- Fields:
- >>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection
- Gene Name:
- CRTC1
- Protein Name:
- CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 23373
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q6UUV9
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q68ED7
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human TORC1 expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- TORC1 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of TORC1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. Flow cytometry: 1:200 - 1:400. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CRTC1;KIAA0616;MECT1;TORC1;WAMTP1;CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 1;Mucoepidermoid carcinoma translocated protein 1;Transducer of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein 1;TORC-1;Transducer of CREB protein 1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 67kD
- References:
- 1. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2007 Jun;46(6):559-63.
2. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2008 Jan 15;180(2):135-9.
3. Biosci Rep. 2009 Apr;29(2):77-87.
- Background:
- disease:A chromosomal aberration involving CRTC1 is found in mucoepidermoid carcinomas, benign Warthin tumors and clear cell hidradenomas. Translocation t(11;19)(q21;p13) with MAML2. The fusion protein consists of the N-terminus of CRTC1 joined to the C-terminus of MAML2. The reciprocal fusion protein consisting of the N-terminus of MAML2 joined to the C-terminus of CRTC1 has been detected in a small number of mucoepidermoid carcinomas.,function:Transcriptional coactivator for CREB1 which activates transcription through both consensus and variant cAMP response element (CRE) sites. Acts as a coactivator, in the SIK/TORC signaling pathway, being active when dephosphorylated and acts independently of CREB1 'Ser-133' phosphorylation. Enhances the interaction of CREB1 with TAF4. Regulates the expression of specific CREB-activated genes such as the steroidogenic gene, StAR. Potent coactivator of PGC1alpha and inducer of mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. Also coactivator for TAX activation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) long terminal repeats (LTR). In the hippocampus, involved in late-phase long-term potentiation (L-LTP) maintenance at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses.,PTM:Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation states of Ser-151 are required for regulating transduction of CREB activity. TORCs are inactive when phosphorylated, and active when dephosphorylated at this site. This primary site of phosphorylation, is regulated by cAMP and calcium levels and is dependent on the phosphorylation of SIKs by LKB1 (By similarity). Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Belongs to the TORC family.,subcellular location:Cytoplasmic when phosphorylated by SIK or AMPK and when sequestered by 14-3-3 proteins (By similarity). Translocated to the nucleus on Ser-151 dephosphorylation, instigated by a number of factors including calcium ion and cAMP levels.,subunit:Binds, as a tetramer, through its N-terminal region, with the bZIP domain of CREB1. 'Arg-314' in the bZIP domain of CREB1 is essential for this interaction. Interaction, via its C-terminal, with TAF4, enhances recruitment of TAF4 to CREB1. Binds HTLV1 Tax.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in adult and fetal brain. Located to specific regions such as the prefrontal cortex and cerebellum. Very low expression in other tissues such as heart, spleen, lung, skeletal muscle, salivary gland, ovary and kidney.,
- Function:
- disease:A chromosomal aberration involving CRTC1 is found in mucoepidermoid carcinomas, benign Warthin tumors and clear cell hidradenomas. Translocation t(11;19)(q21;p13) with MAML2. The fusion protein consists of the N-terminus of CRTC1 joined to the C-terminus of MAML2. The reciprocal fusion protein consisting of the N-terminus of MAML2 joined to the C-terminus of CRTC1 has been detected in a small number of mucoepidermoid carcinomas.,function:Transcriptional coactivator for CREB1 which activates transcription through both consensus and variant cAMP response element (CRE) sites. Acts as a coactivator, in the SIK/TORC signaling pathway, being active when dephosphorylated and acts independently of CREB1 'Ser-133' phosphorylation. Enhances the interaction of CREB1 with TAF4. Regulates the expression of specific CREB-activated genes such as the steroidogenic gene, StAR. Potent coactivator
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasmic when phosphorylated by SIK or AMPK and when sequestered by 14-3-3 proteins (PubMed:16817901). Translocated to the nucleus on Ser-151 dephosphorylation, instigated by a number of factors including calcium ion and cAMP levels (PubMed:15589160). Light stimulation triggers a nuclear accumulation in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in adult and fetal brain. Located to specific regions such as the prefrontal cortex and cerebellum. Very low expression in other tissues such as heart, spleen, lung, skeletal muscle, salivary gland, ovary and kidney.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using TORC1 Monoclonal Antibody against CRTC1-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 cell lysate.
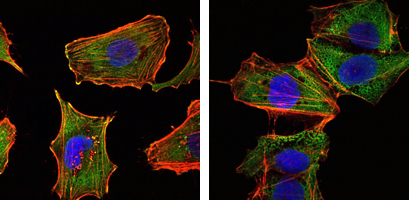
- Immunofluorescence analysis of U251 (left) and NTERA2 (right) cells using TORC1 Monoclonal Antibody (green). Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with DY-554 phalloidin. Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye.

- Flow cytometric analysis of K562 cells using TORC1 Monoclonal Antibody (green) and negative control (purple).