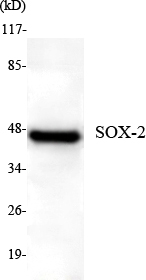
SOX-2 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0594
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- SOX-2
- Fields:
- >>Hippo signaling pathway;>>Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells
- Gene Name:
- SOX2
- Protein Name:
- Transcription factor SOX-2
- Human Gene Id:
- 6657
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P48431
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P48432
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human SOX-2 expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- SOX-2 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of SOX-2 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SOX2;Transcription factor SOX-2
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 34kD
- References:
- 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Nov 25;105(47):18396-401.
2. J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 28;283(48):33730-5.
3. Nature. 2008 Oct 23;455(7216):1124-8.
- Background:
- SRY-box 2(SOX2) Homo sapiens This intronless gene encodes a member of the SRY-related HMG-box (SOX) family of transcription factors involved in the regulation of embryonic development and in the determination of cell fate. The product of this gene is required for stem-cell maintenance in the central nervous system, and also regulates gene expression in the stomach. Mutations in this gene have been associated with optic nerve hypoplasia and with syndromic microphthalmia, a severe form of structural eye malformation. This gene lies within an intron of another gene called SOX2 overlapping transcript (SOX2OT). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SOX2 are the cause of microphthalmia syndromic type 3 (MCOPS3) [MIM:206900]. Microphthalmia is a clinically heterogeneous disorder of eye formation, ranging from small size of a single eye to complete bilateral absence of ocular tissues (anophthalmia). In many cases, microphthalmia/anophthalmia occurs in association with syndromes that include non-ocular abnormalities. MCOPS3 is characterized by the rare association of malformations including uni- or bilateral anophthalmia or microphthalmia, and esophageal atresia with trachoesophageal fistula.,function:Transcription factor that forms a trimeric complex with OCT4 on DNA and controls the expression of a number of genes involved in embryonic development such as YES1, FGF4, UTF1 and ZFP206. Critical for early embryogenesis and for embryonic stem cell pluripotency.,online information:Sox2 entry,PTM:Sumoylation inhibits bin
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus speckle . Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Acetylation contributes to its nuclear localization and deacetylation by HDAC3 induces a cytoplasmic delocalization (By similarity). Colocalizes in the nucleus with ZNF208 isoform KRAB-O and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) (By similarity). Colocalizes with SOX6 in speckles. Colocalizes with CAML in the nucleus (By similarity). Nuclear import is facilitated by XPO4, a protein that usually acts as a nuclear export signal receptor (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Fetal brain,Lung,Retina,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
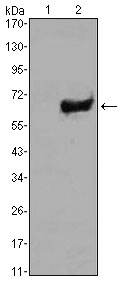
- Western Blot analysis using SOX-2 Monoclonal Antibody against HEK293 (1) and SOX2-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate.
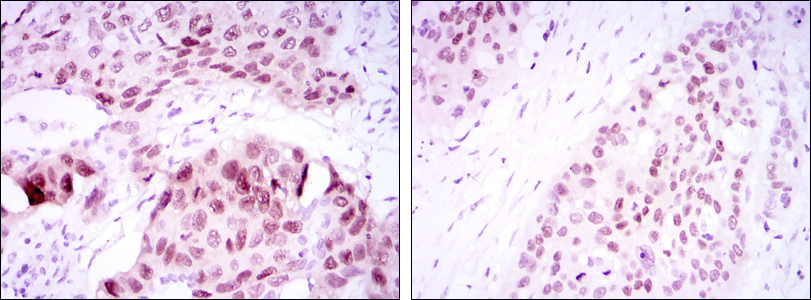
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded lung cancer tissues (left) and esophageal cancer tissues (right) with DAB staining using SOX-2 Monoclonal Antibody.
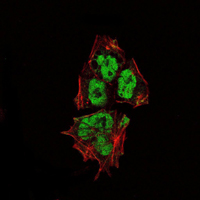
- Immunofluorescence analysis of NTERA-2 cells using SOX-2 Monoclonal Antibody (green). Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin.