Total SIAH1 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA4368C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
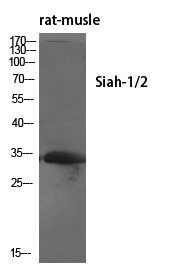
- SIAH1/2
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8IUQ4/O43255
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- domain:The RING-type zinc finger domain is essential for ubiquitin ligase activity.,domain:The SBD domain (substrate-binding domain) mediates the homodimerization and the interaction with substrate proteins. It is related to the TRAF family.,function:E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. E3 ubiquitin ligases accept ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. Mediates E3 ubiquitin ligase activity either through direct binding to substrates or by functioning as the essential RING domain subunit of larger E3 complexes. Triggers the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of many substrates, including proteins involved in transcription regulation (MYB, POU2AF1, PML and RBBP8), a cell surface receptor (DCC), cytoplasmic signal transduction molecules (TIEG1 and NUMB), an antiapoptotic protein (BAG1), a microtubule motor protein (KIF22), a protein involved in synaptic vesicle function in neurons (SYP), a structural protein (CTNNB1) and SNCAIP. It is thereby involved in many cellular processes such as apoptosis, tumor suppression, cell cycle, axon guidance, transcription regulation, spermatogenesis and TNF-alpha signaling. Has some overlapping function with SIAH2. Induces apoptosis in cooperation with PEG3.,induction:May be induced by TP53/p53, suggesting that it may be required to modulate TP53 response. The relevance of such activity in vivo is however unclear and may not exist.,pathway:Protein modification; protein ubiquitination.,similarity:Belongs to the SINA (Seven in absentia) family.,similarity:Contains 1 RING-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 SIAH-type zinc finger.,subcellular location:Predominantly cytoplasmic. Partially nuclear.,subunit:Homodimer. Interacts with group 1 glutamate receptors GRM1 and GRM5. Interacts with DAB1, which may inhibit its activity. Interacts with UBE2E2. Interacts with PEG3 (By similarity). Component of some large E3 complex composed of UBE2D1, SIAH1, CACYBP/SIP, SKP1, APC and TBL1X. Interacts with UBE2I. Interacts with alpha-tubulin. Interacts with PEG10, which may inhibit its activity. Interacts with KHDRBS3.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed at low level. Down-regulated in advanced hepatocellular carcinomas.,
- Function:
- cell morphogenesis, cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, proteolysis, ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, apoptosis, cell motion, cell cycle, gamete generation, spermatogenesis, axonogenesis, axon guidance, cell death, macromolecule catabolic process, programmed cell death, death, protein ubiquitination, modification-dependent protein catabolic process, sexual reproduction, cell projection organization, protein catabolic process, neuron differentiation, neuron projection development, protein modification by small protein conjugation, multicellular organism reproduction, cellular component morphogenesis, cell part morphogenesis, protein ubiquitination during ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, modification-dependent macromolecule catabolic process, cellular protein catabolic process, cellular macromolecule catabolic process, male gamete generation, reprodu
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Predominantly cytoplasmic. Partially nuclear.
- Expression:
- Widely expressed at a low level. Down-regulated in advanced hepatocellular carcinomas.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs