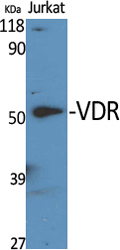
Total Vitamin D Receptor Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA4321C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Gene Name:
- VDR
- Human Gene Id:
- 7421
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P11473
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P48281
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 1)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- caution:It is uncertain whether Met-1 or Met-4 is the initiator.,disease:Defects in VDR are the cause of type IIA rickets [MIM:277440]; also known as hypocalcemic vitamin D-resistant rickets (HVDRR). HVDRR is most frequently an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe rickets, hypocalcemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism.,domain:Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal steroid-binding domain.,function:Nuclear hormone receptor. Transcription factor that mediates the action of vitamin D3 by controlling the expression of hormone sensitive genes. Regulates transcription of hormone sensitive genes via its association with the WINAC complex, a chromatin-remodeling complex. Recruited to promoters via its interaction with the WINAC complex subunit BAZ1B/WSTF, which mediates the interaction with acetylated histones, an essential step for VDR-promoter association. Plays a central role in calcium homeostasis.,online information:The Singapore human mutation and polymorphism database,polymorphism:Genetic variations in VDR may determine Mycobacterium tuberculosis susceptibility [MIM:607948].,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain.,subunit:Homodimer in the absence of bound vitamin D3. Heterodimer with RXRA after vitamin D3 binding. Interacts with SMAD3. Interacts with MED1, NCOA1, NCOA2, NCOA3 and NCOA6 coactivators, leading to a strong increase of transcription of target genes. Interacts (in a ligand-dependent manner) with BAZ1B/WSTF.,
- Function:
- negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, skeletal system development, placenta development, maternal placenta development, reproductive developmental process, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, ion transport, cation transport, calcium ion transport, cellular ion homeostasis, cellular calcium ion homeostasis, cellular metal ion homeostasis, induction of apoptosis, intracellular signaling cascade, female pregnancy, response to nutrient,digestion, negative regulation of cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals, induction of apoptosis by hormones, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, response to extracellular stimulus, regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, negative regulation of specific transcription from RNA pol
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Localizes mainly to the nucleus (PubMed:28698609, PubMed:12145331). Localization to the nucleus is enhanced by vitamin D3. .
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs