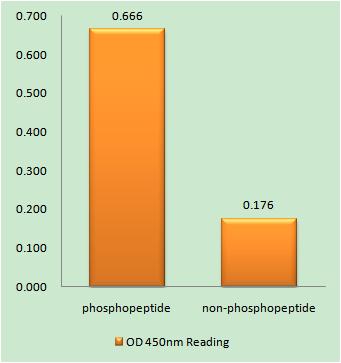
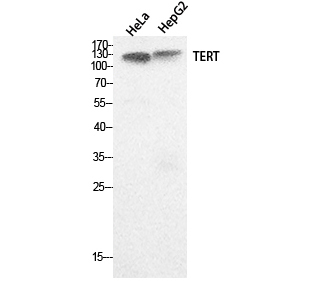
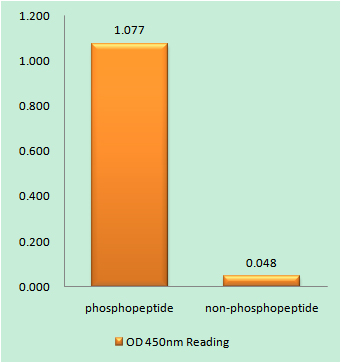
Total Telomerase Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA4301C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Gene Name:
- TERT
- Human Gene Id:
- 7015
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O14746
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O70372
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Telomerase reverse transcriptase (EC 2.7.7.49) (HEST2) (Telomerase catalytic subunit) (Telomerase-associated protein 2) (TP2)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- catalytic activity:Deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1).,disease:Activation of telomerase has been implicated in cell immortalization and cancer cell pathogenesis.,disease:Defects in TERT are a cause of dyskeratosis congenita autosomal dominant (ADDKC) [MIM:127550]; also known as dyskeratosis congenita Scoggins type. ADDKC is a rare, progressive bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by the triad of reticulated skin hyperpigmentation, nail dystrophy, and mucosal leukoplakia. Early mortality is often associated with bone marrow failure, infections, fatal pulmonary complications, or malignancy.,disease:Defects in TERT are associated with susceptibilty to aplastic anemia (AA) [MIM:609135]. AA is a rare disease in which the reduction of the circulating blood cells results from damage to the stem cell pool in bone marrow. In most patients, the stem cell lesion is caused by an autoimmune attack. T-lymphocytes, activated by an endogenous or exogenous, and most often unknown antigenic stimulus, secrete cytokines, including IFN-gamma, which would in turn be able to suppress hematopoiesis.,disease:Defects in TERT increases susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [MIM:178500]. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is an adult-onset, lethal, scarring lung disease of unknown etiology. Its clinical features are shortness of breath, radiographically evident diffuse pulmonary infiltrates, and varying degrees in inflammation, fibrosis, or both on biopsy. It is rapidly progressive and characterized by sequential acute lung injury with subsequent scarring and endstage lung disease.,disease:Genetic variations in TERT are associated with coronary artery disease (CAD).,function:Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme essential for the replication of chromosome termini in most eukaryotes. It elongates telomeres. It is a reverse transcriptase that adds simple sequence repeats to chromosome ends by copying a template sequence within the RNA component of the enzyme.,similarity:Belongs to the reverse transcriptase family. Telomerase subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 reverse transcriptase domain.,subunit:Catalytic subunit of the telomerase holoenzyme complex at least composed of TERT, DKC1, WDR79/TCAB1, NOP10, NHP2, GAR1, TEP1, EST1A, POT1 and a telomerase RNA template component (TERC). Interacts with PINX1 and MCRS1.,
- Function:
- telomere maintenance, DNA metabolic process, DNA replication, RNA-dependent DNA replication, anti-apoptosis,telomere maintenance via telomerase, aging, senescence, telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening, regulation of cell death, DNA strand elongation, telomere organization, telomere assembly, telomere formation via telomerase,homeostatic process, regulation of apoptosis, negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death,negative regulation of programmed cell death, chromosome organization, anatomical structure homeostasis, negative regulation of cell death,
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus, nucleolus . Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus. Chromosome, telomere. Cytoplasm. Nucleus, PML body. Shuttling between nuclear and cytoplasm depends on cell cycle, phosphorylation states, transformation and DNA damage. Diffuse localization in the nucleoplasm. Enriched in nucleoli of certain cell types. Translocated to the cytoplasm via nuclear pores in a CRM1/RAN-dependent manner involving oxidative stress-mediated phosphorylation at Tyr-707. Dephosphorylation at this site by SHP2 retains TERT in the nucleus. Translocated to the nucleus by phosphorylation by AKT.
- Expression:
- Expressed at a high level in thymocyte subpopulations, at an intermediate level in tonsil T-lymphocytes, and at a low to undetectable level in peripheral blood T-lymphocytes.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs