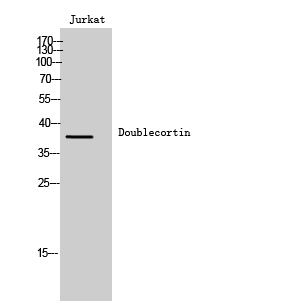
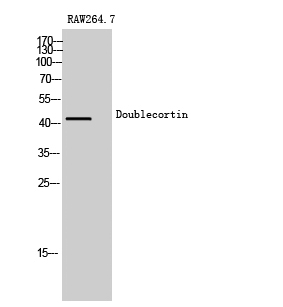
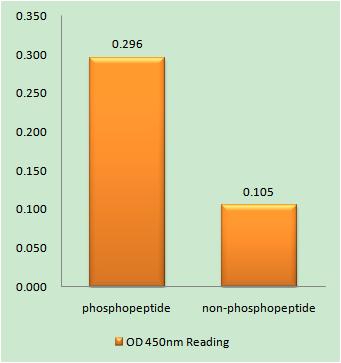
Total Doublecortin Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA4076C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- DCX
- Human Gene Id:
- 1641
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O43602
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O88809
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9ESI7
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Neuronal migration protein doublecortin (Doublin) (Lissencephalin-X) (Lis-X)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- alternative products:Isoform LIS-XA possesses an alternative exon in 5' and is then translated from an upstream initiation codon. Isoform LIS-XB, isoform LIS-XC and isoform LIS-XD translation starts at the downstream initiation codon, leading to the absence of the 81 first amino acids. Isoform LIS-XC and isoform LIS-XD differ from isoform LIS-XB by a five amino acids and a one amino acid-insertion respectively,disease:A chromosomal aberration involving DCX is found in lissencephaly. Translocation t(X;2)(q22.3;p25.1).,disease:Defects in DCX are the cause of lissencephaly X-linked type 1 (LISX1) [MIM:300067]; also called X-LIS or LIS. LISX1 is a classic lissencephaly characterized by mental retardation and seizures that are more severe in male patients. Affected boys show an abnormally thick cortex with absent or severely reduced gyri. Clinical manifestations include feeding problems, abnormal muscular tone, seizures and severe to profound psychomotor retardation. Female patients display a less severe phenotype referred to as 'doublecortex'.,disease:Defects in DCX are the cause of subcortical band heterotopia X-linked (SBHX) [MIM:300067]; also known as double cortex or subcortical laminar heterotopia (SCLH). SBHX is a mild brain malformation of the lissencephaly spectrum. It is characterized by bilateral and symmetric plates or bands of gray matter found in the central white matter between the cortex and cerebral ventricles, cerebral convolutions usually appearing normal.,function:Seems to be required for initial steps of neuronal dispersion and cortex lamination during cerebral cortex development. May act by competing with the putative neuronal protein kinase DCAMKL1 in binding to a target protein. May in that way participate in a signaling pathway that is crucial for neuronal interaction before and during migration, possibly as part of a calcium ion-dependent signal transduction pathway. May be part with LIS-1 of an overlapping, but distinct, signaling pathways that promote neuronal migration.,similarity:Contains 2 doublecortin domains.,subunit:Interacts with tubulin.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in neuronal cells of fetal brain (in the majority of cells of the cortical plate, intermediate zone and ventricular zone), but not expressed in other fetal tissues. In the adult, highly expressed in the brain frontal lobe, but very low expression in other regions of brain, and not detected in heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscles, kidney and pancreas.,
- Function:
- cell morphogenesis, cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, neuron migration, cell motion, intracellular signaling cascade, axonogenesis, regulation of cell size, cell growth, dendrite development, cell migration, central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis, central nervous system neuron differentiation, central nervous system neuron development, central nervous system neuron axonogenesis, cell projection organization, neuron differentiation, neuron projection development, regulation of cellular component size, cellular component morphogenesis, cell part morphogenesis, growth, developmental cell growth, developmental growth, neuron development, cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation, axon extension, neuron projection morphogenesis, dendrite morphogenesis, cell projection morphogenesis, cell motility, localization of cell,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Cell projection, neuron projection . Localizes at neurite tips. .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in neuronal cells of fetal brain (in the majority of cells of the cortical plate, intermediate zone and ventricular zone), but not expressed in other fetal tissues. In the adult, highly expressed in the brain frontal lobe, but very low expression in other regions of brain, and not detected in heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscles, kidney and pancreas.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs