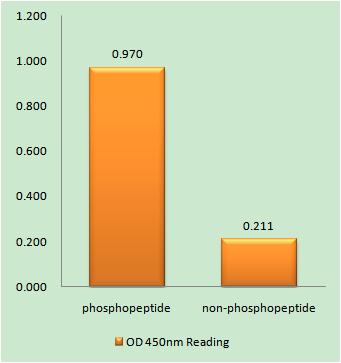
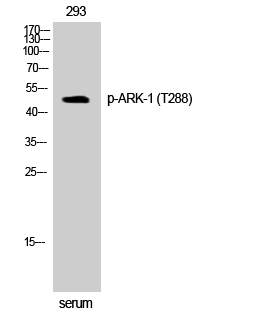
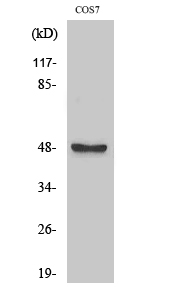
Total AurA Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA4005C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- AURKA
- Human Gene Id:
- 6790
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O14965
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P97477
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P59241
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Aurora kinase A (EC 2.7.11.1) (Aurora 2) (Aurora/IPL1-related kinase 1) (ARK-1) (Aurora-related kinase 1) (hARK1) (Breast tumor-amplified kinase) (Serine/threonine-protein kinase 15) (Serine/threonine-protein kinase 6) (Serine/threonine-protein kinase aurora-A)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein.,caution:Although authors have considered STK6 and STK15 as two different proteins, it is clear that they are the same protein.,disease:Defects in AURKA are responsible for numerical centrosome aberrations including aneuploidy.,function:May play a role in cell cycle regulation during anaphase and/or telophase, in relation to the function of the centrosome/spindle pole region during chromosome segregation. May be involved in microtubule formation and/or stabilization. Phosphorylates ARHGEF2 and BORA.,PTM:Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. Aurora subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,subcellular location:Localizes on centrosomes in interphase cells and at each spindle pole in mitosis.,subunit:Interacts with TACC1 and CPEB1. Interacts with its substrates BORA and ARHGEF2.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in testis and weakly in skeletal muscle, thymus and spleen. Also highly expressed in colon, ovarian, prostate, neuroblastoma, breast and cervical cancer cell lines. Expression is cell-cycle regulated, low in G1/S, accumulates during G2/M, and decreases rapidly after.,
- Function:
- M phase of mitotic cell cycle, microtubule cytoskeleton organization, mitotic cell cycle, M phase, nuclear division, protein amino acid phosphorylation, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, cytoskeleton organization,microtubule-based process, cell cycle, spindle organization, mitosis, intracellular signaling cascade, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, response to organic substance, posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, phosphorylation, second-messenger-mediated signaling, cell cycle process, cell cycle phase,regulation of protein stability, response to estradiol stimulus, response to estrogen stimulus, phosphoinositide-mediated signaling, organelle fission, response to steroid hormone stimulus,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole . Cell projection, neuron projection . Detected at the neurite hillock in developing neurons (By similarity). Localizes at the centrosome in mitotic cells from early prophase until telophase, but also localizes to the spindle pole MTs from prophase to anaphase (PubMed:9606188, PubMed:17229885, PubMed:21225229). Colocalized with SIRT2 at centrosome (PubMed:22014574). Moves to the midbody during both telophase and cytokinesis (PubMed:17726514). Associates with both the pericentriolar material (PCM) and centrioles (PubMed:22014574). The localization to the spindle
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in testis and weakly in skeletal muscle, thymus and spleen. Also highly expressed in colon, ovarian, prostate, neuroblastoma, breast and cervical cancer cell lines.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs