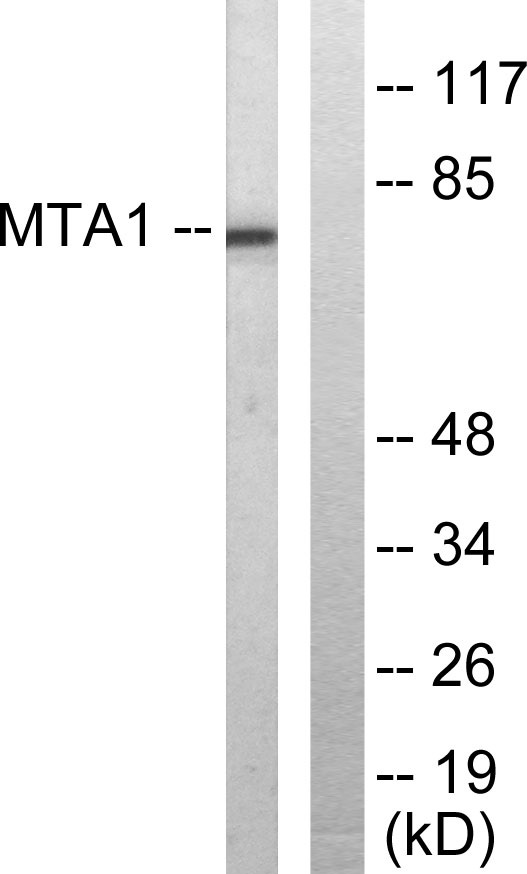
Total MTA1 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3709C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- MTA1
- Human Gene Id:
- 9112
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q13330
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8K4B0
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q62599
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Metastasis-associated protein MTA1
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- developmental stage:Highly expressed in metastatic cells.,function:May be involved in the regulation of gene expression by covalent modification of histone proteins. The long isoform is a corepressor of estrogen receptor (ER). The short isoform binds to ER and sequesters it in the cytoplasm and enhances non-genomic responses of ER.,miscellaneous:The short isoform contains a Leu-Arg-Ile-Leu-Leu motif (ER binding motif).,similarity:Contains 1 BAH domain.,similarity:Contains 1 ELM2 domain.,similarity:Contains 1 GATA-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 SANT domain.,subunit:Component of the nucleosome-remodeling and histone-deacetylase multiprotein complex (NuRD). Interacts with HDAC1 and ITGB3BP/CENPR.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed. High expression in brain, ovaries, adrenal glands and virgin mammary glands. Higher in tumors than in adjacent normal tissue from the same individual.,
- Function:
- regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription, regulation of RNA metabolic process,
- Subcellular Location:
- [Isoform Short]: Cytoplasm.; [Isoform Long]: Nucleus. Nucleus envelope. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Associated with microtubules. Localization at the nuclear envelope is TPR-dependent.
- Expression:
- Widely expressed. High expression in brain, liver, kidney, and cardiac muscle, ovaries, adrenal glands and virgin mammary glands. Higher in tumors than in adjacent normal tissue from the same individual. Up-regulated in a wide variety of cancers including breast, liver, ovarian, and colorectal cancer and its expression levels are closely correlated with tumor aggressiveness and metastasis.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs