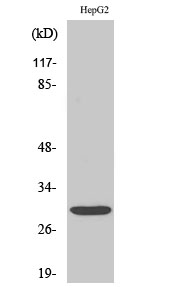
Total Myf-6 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3566C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- MYF6
- Human Gene Id:
- 4618
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P23409
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P15375
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P19335
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Myogenic factor 6 (Myf-6) (Class C basic helix-loop-helix protein 4) (bHLHc4) (Muscle-specific regulatory factor 4)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- disease:Defects in MYF6 may be a cause of centronuclear myopathy autosomal dominant (ADCNM) [MIM:160150]; also known as autosomal dominant myotubular myopathy. Centronuclear myopathies are congenital muscle disorders characterized by progressive muscular weakness and wasting involving mainly limb girdle, trunk, and neck muscles. It may also affect distal muscles. Weakness may be present during childhood or adolescence or may not become evident until the third decade of life. Ptosis is a frequent clinical feature. The most prominent histopathologic features include high frequency of centrally located nuclei in muscle fibers not secondary to regeneration, radial arrangement of sarcoplasmic strands around the central nuclei, and predominance and hypotrophy of type 1 fibers.,function:Involved in muscle differentiation (myogenic factor). Induces fibroblasts to differentiate into myoblasts. Probable sequence specific DNA-binding protein.,similarity:Contains 1 basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain.,subunit:Efficient DNA binding requires dimerization with another bHLH protein.,tissue specificity:Skeletal muscle.,
- Function:
- somitogenesis, regionalization, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, pattern specification process, muscle organ development, skeletal muscle tissue development, response to wounding, embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, anterior/posterior pattern formation, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, striated muscle tissue development, negative regulation of transcription, regeneration, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regu
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus.
- Expression:
- Skeletal muscle.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs