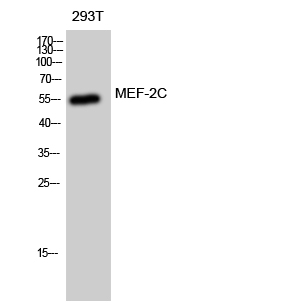
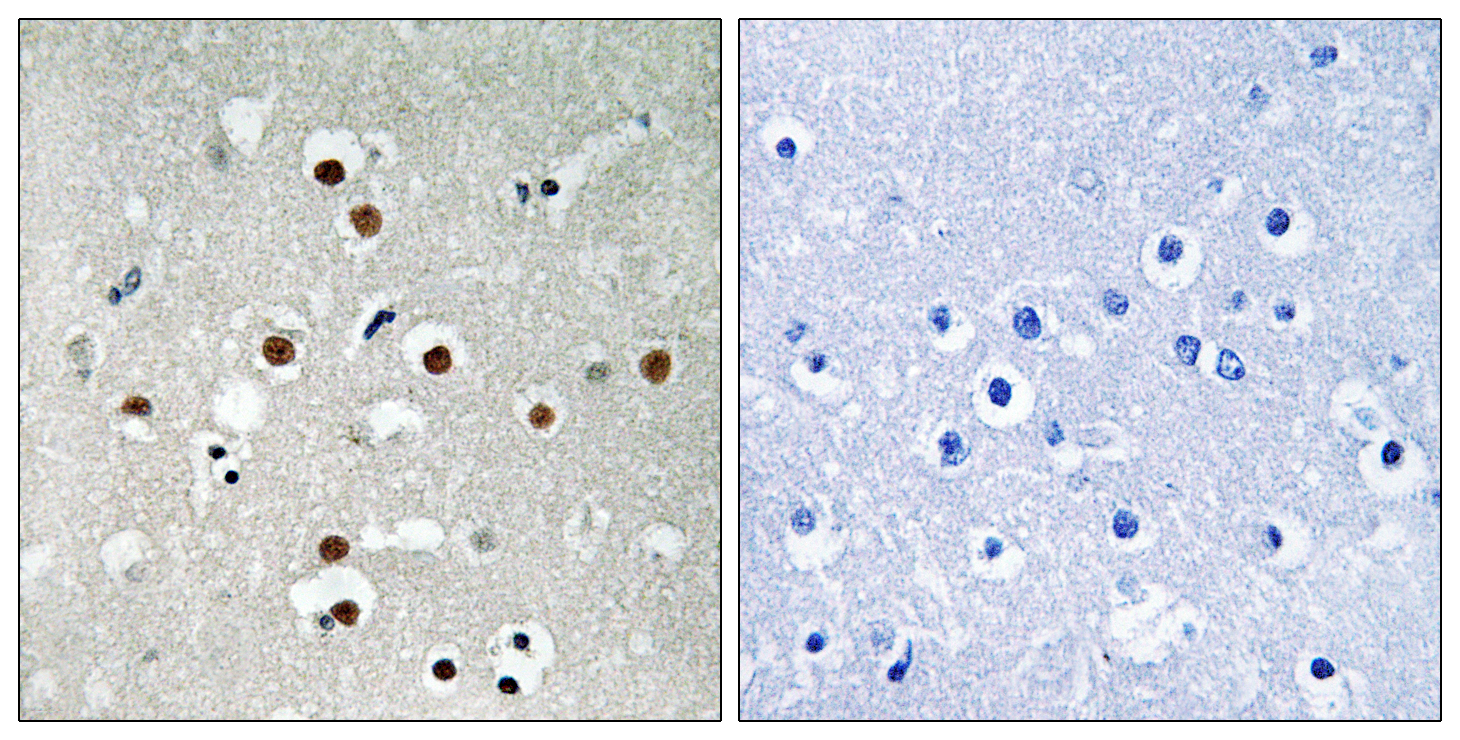
Phospho MEF2C (S396) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1753C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Gene Name:
- MEF2C
- Human Gene Id:
- 4208
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q06413
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8CFN5
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,developmental stage:Expression is highest during the early stages of postnatal development, at later stages levels greatly decrease.,domain:The beta domain, missing in a number of isoforms, is required for enhancement of transcriptional activity.,function:Transcription activator which binds specifically to the MEF2 element present in the regulatory regions of many muscle-specific genes. Controls cardiac morphogenesis and myogenesis, and is also involved in vascular development. May also be involved in neurogenesis and in the development of cortical architecture (By similarity). Isoform 3 and isoform 4, which lack the repressor domain, are more active than isoform 1 and isoform 2.,PTM:Acetylated by p300 on several sites in diffentiating myocytes. Acetylation on Lys-4 increases DNA binding and transactivation.,PTM:Phosphorylation on Ser-59 enhances DNA binding activity (By similarity). Phosphorylation on Ser-396 is required for Lys-391 sumoylation and inhibits transcriptional activity.,PTM:Proteolytically cleaved in cerebellar granule neurons, probably by caspase 7, following neurotoxicity. Preferentially cleaves the CDK5-mediated hyperphosphorylated form which leads to neuron apoptosis and transcriptional inactivation.,PTM:Sumoylated on Lys-391 by SUMO2 but not by SUMO1 represses transcriptional activity.,similarity:Belongs to the MEF2 family.,similarity:Contains 1 MADS-box domain.,similarity:Contains 1 Mef2-type DNA-binding domain.,subunit:Forms a complex with class II HDACs in undifferentiating cells. On myogenic differentiation, HDACs are released into the cytoplasm allowing MEF2s to interact with other proteins for activation. Interacts with EP300 in differentiating cells; the interaction acetylates MEF2C leading to increased DNA binding and activation. Interacts with HDAC7 and CARM1 (By similarity). Interacts with HDAC4, HDAC7 AND HDAC9; the interaction WITH HDACs represses transcriptional activity.,tissue specificity:Expressed in brain and skeletal muscle.,
- Function:
- negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, apoptosis, anti-apoptosis, muscle organ development, cell death, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process,regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, negative regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, regulation of cell
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Cytoplasm, sarcoplasm .
- Expression:
- Expressed in brain and skeletal muscle.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs