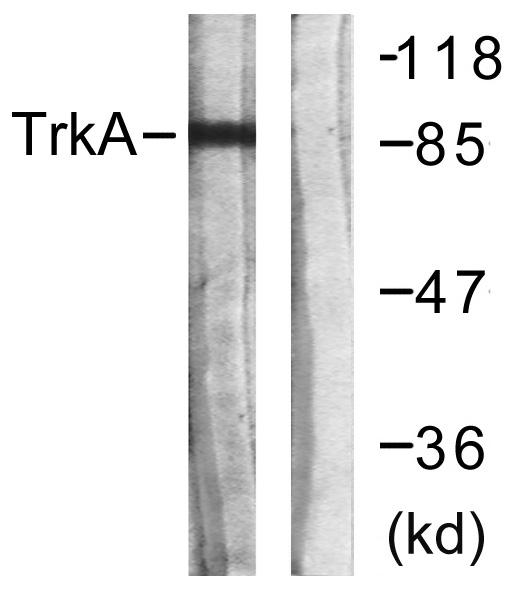
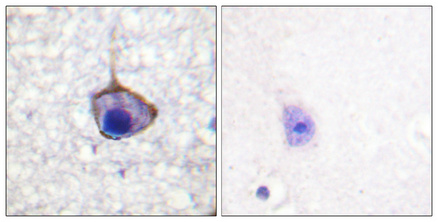
Phospho Trk A (Y701) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1693C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- NTRK1
- Human Gene Id:
- 4914
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P04629
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q3UFB7
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P35739
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- High affinity nerve growth factor receptor (EC 2.7.10.1) (Neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1) (TRK1-transforming tyrosine kinase protein) (Tropomyosin-related kinase A) (Tyrosine kinase receptor) (Tyrosine kinase receptor A) (Trk-A) (gp140trk) (p140-TrkA)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- alternative products:Both isoforms have similar biological properties,catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,caution:The sequence shown here is derived from an Ensembl automatic analysis pipeline and should be considered as preliminary data.,disease:Chromosomal aberrations involving NTRK1 are a cause of thyroid papillary carcinoma (PACT) [MIM:188550]. Intrachromosomal rearrangement that links the protein kinase domain of NTRK1 to the 5'-end of the TPR gene forms the fusion protein TRK-T1. TRK-T1 is a 55 kDa protein reacting with antibodies against the C-terminus of the NTRK1 protein.,disease:Chromosomal aberrations involving NTRK1 are a cause of thyroid papillary carcinoma (PACT) [MIM:188550]. Translocation t(1;3)(q21;q11) with TFG generates the TRKT3 (TRK-T3) transcript by fusing TFG to the 3'-end of NTRK1; a rearrangement with TPM3 generates the TRK transcript by fusing TPM3 to the 3'-end of NTRK1.,disease:Defects in NTRK1 are a cause of congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA) [MIM:256800]. CIPA is characterized by a congenital insensitivity to pain, anhidrosis (absence of sweating), absence of reaction to noxious stimuli, self-mutilating behavior, and mental retardation. This rare autosomal recessive disorder is also known as congenital sensory neuropathy with anhidrosis or hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV or familial dysautonomia type II.,domain:The extracellular domain mediates interaction with NGFR.,domain:The transmembrane domain mediates interaction with KIDINS220.,function:Required for high-affinity binding to nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-3 and neurotrophin-4/5 but not brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Known substrates for the Trk receptors are SHC1, PI 3-kinase, and PLC-gamma-1. Has a crucial role in the development and function of the nociceptive reception system as well as establishment of thermal regulation via sweating. Activates ERK1 by either SHC1- or PLC-gamma-1-dependent signaling pathway.,PTM:Ligand-mediated auto-phosphorylation. Interaction with SQSTM1 is phosphotyrosine-dependent.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Insulin receptor subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 2 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.,similarity:Contains 3 LRR (leucine-rich) repeats.,subcellular location:Endocytosed to the endosomes upon treatment of cells with NGF.,subunit:Exists in a dynamic equilibrium between monomeric (low affinity) and dimeric (high affinity) structures. Binds SH2B2. Interacts with SQSTM1 which bridges NTRK1 to NGFR. Interacts with KIDINS220 and NGFR. Can form a ternary complex with NGFR and KIDINS220 and this complex is affected by the expression levels of KIDINS220. An increase in KIDINS220 expression leads to a decreased association of NGFR and NTRK1.,tissue specificity:Isoform TrkA-II is primarily expressed in neuronal cells; isoform TrkA-I is found in non-neuronal tissues.,
- Function:
- cell activation, immune system development, leukocyte differentiation, regulation of nucleotide metabolic process,protein amino acid phosphorylation, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, activation of adenylate cyclase activity, intracellular signaling cascade,small GTPase mediated signal transduction, Ras protein signal transduction, regulation of cell death, phosphorylation,hemopoiesis, lymphocyte differentiation, neuron differentiation, B cell differentiation, regulation of cyclic nucleotide metabolic process, regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process, regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process,regulation of cAMP metabolic process, regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process, regulation of
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Early endosome membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Late endosome membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Recycling endosome membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Rapidly internalized after NGF binding (PubMed:1281417). Internalized to endosomes upon binding of NGF or NTF3 and further transported to the cell body via a retrograde axonal transport. Localized at cell membrane and early endosomes before nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulation. Recruited to late endosomes after NGF stimulation. Colocalized with RAPGEF2 at late endosomes. .
- Expression:
- Isoform TrkA-I is found in most non-neuronal tissues. Isoform TrkA-II is primarily expressed in neuronal cells. TrkA-III is specifically expressed by pluripotent neural stem and neural crest progenitors.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs