Phospho HDAC5 (S498) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1581C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Gene Name:
- HDAC5
- Human Gene Id:
- 10014
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9UQL6
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9Z2V6
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
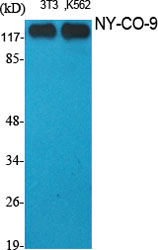
- Histone deacetylase 5 (HD5) (EC 3.5.1.98) (Antigen NY-CO-9)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- catalytic activity:Hydrolysis of an N(6)-acetyl-lysine residue of a histone to yield a deacetylated histone.,domain:The nuclear export sequence mediates the shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.,function:Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Involved in muscle maturation by repressing transcription of myocyte enhancer MEF2C. During muscle differentiation, it shuttles into the cytoplasm, allowing the expression of myocyte enhancer factors.,PTM:Phosphorylated by CaMK at Ser-259 and Ser-498. The phosphorylation is required for the export to the cytoplasm.,PTM:Ubiquitinated. Polyubiquitination however does not lead to its degradation.,similarity:Belongs to the histone deacetylase family. Type 2 subfamily.,subcellular location:Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. In muscle cells, it shuttles into the cytoplasm during myocyte differentiation. The export to cytoplasm depends on the interaction with a 14-3-3 chaperone protein and is due to its phosphorylation at Ser-259 and Ser-498 by CaMK.,subunit:Interacts with AHRR (By similarity). Interacts with BCOR, HDAC7, HDAC9, CTBP1, MEF2C, NCOR2, NRIP1, PHB2 and a 14-3-3 chaperone protein. Interacts with KDM5B.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous.,
- Function:
- negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, cell activation, immune system development,leukocyte differentiation, muscle system process, chromatin organization, chromatin remodeling, chromatin silencing,transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter,protein amino acid deacetylation, defense response, inflammatory response, heart development, response to wounding, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, response to organic substance, regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter,negative regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of ma
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. In muscle cells, it shuttles into the cytoplasm during myocyte differentiation. The export to cytoplasm depends on the interaction with a 14-3-3 chaperone protein and is due to its phosphorylation at Ser-259 and Ser-498 by AMPK, CaMK1 and SIK1.
- Expression:
- Ubiquitous.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs

.jpg)