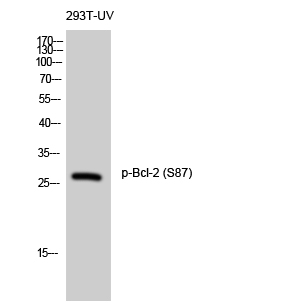
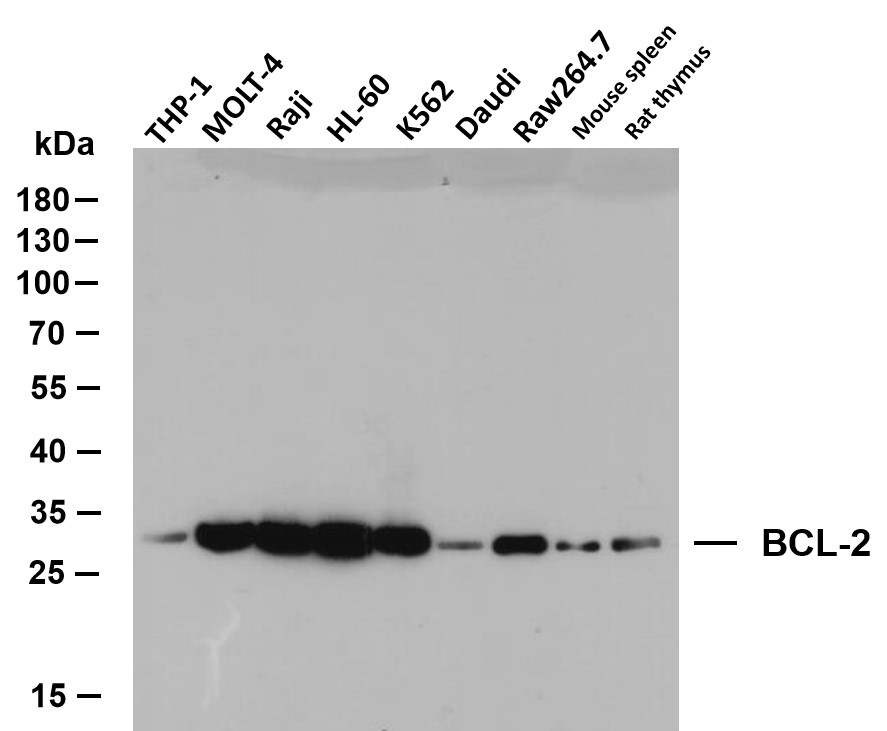
Phospho Bcl-2 (T56) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1032C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Gene Name:
- BCL2
- Human Gene Id:
- 596
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P10415
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P10417
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- disease:A chromosomal aberration involving BCL2 may be a cause of follicular lymphoma (FL) [MIM:151430]; also known as type II chronic lymphatic leukemia. Translocation t(14;18)(q32;q21) with immunoglobulin gene regions. BCL2 mutations found in non-Hodgkin lymphomas carrying the chromosomal translocation could be attributed to the Ig somatic hypermutation mechanism resulting in nucleotide transitions.,domain:The BH4 motif is required for anti-apoptotic activity and for interaction with RAF-1.,function:Suppresses apoptosis in a variety of cell systems including factor-dependent lymphohematopoietic and neural cells. Regulates cell death by controlling the mitochondrial membrane permeability. Appears to function in a feedback loop system with caspases. Inhibits caspase activity either by preventing the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria and/or by binding to the apoptosis-activating factor (APAF-1).,online information:Bcl-2 entry,PTM:Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation on Ser-70 regulates anti-apoptotic activity. Growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation on Ser-70 by PKC is required for the anti-apoptosis activity and occurs during the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. In the absence of growth factors, BCL2 appears to be phosphorylated by other protein kinases such as ERKs and stress-activated kinases. Dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A).,PTM:Proteolytically cleaved by caspases during apoptosis. The cleaved protein, lacking the BH4 motif, has pro-apoptotic activity, causes the release of cytochrome c into the cytosol promoting further caspase activity.,similarity:Belongs to the Bcl-2 family.,subunit:Forms homodimers, and heterodimers with BAX, BAD, BAK and Bcl-X(L). Heterodimerization with BAX requires intact BH1 and BH2 motifs, and is necessary for anti-apoptotic activity (By similarity). Also interacts with APAF1, RAF-1, TP53BP2, BBC3, BCL2L1, MRPL41 and BNIPL. Binding to FKBP8 seems to target BCL2 to the mitochondria and probably interferes with the binding of BCL2 to its targets.,tissue specificity:Expressed in a variety of tissues.,
- Function:
- G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle, mitotic cell cycle, response to reactive oxygen species, cell morphogenesis, cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, response to acid, skeletal system development, ossification, ovarian follicle development, regulation of cell growth, urogenital system development, metanephros development, ureteric bud development, branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis, behavioral fear response, response to hypoxia,morphogenesis of a branching structure, cell activation, leukocyte homeostasis, B cell homeostasis, kidney development, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, tissue homeostasis, regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, hair follicle development, regulation of cell-matrix adhesion, morphogenesis of an epithelium, behavioral defense response, hemopoietic progenitor c
- Subcellular Location:
- Mitochondrion outer membrane ; Single-pass membrane protein . Nucleus membrane ; Single-pass membrane protein . Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Single-pass membrane protein . Cytoplasm .
- Expression:
- Expressed in a variety of tissues.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs