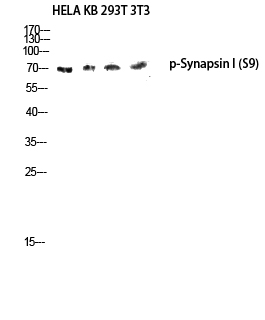
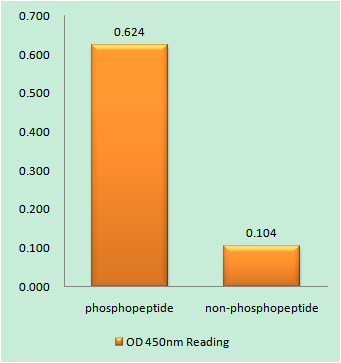
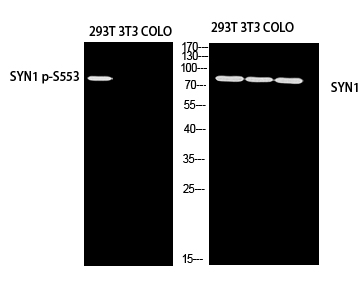
Synapsin I Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4482
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Synapsin I
- Gene Name:
- SYN1
- Protein Name:
- Synapsin-1
- Human Gene Id:
- 6853
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P17600
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 20964
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O88935
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24949
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P09951
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Synapsin1. AA range:26-75
- Specificity:
- Synapsin I Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Synapsin I protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SYN1;Synapsin-1;Brain protein 4.1;Synapsin I
- Observed Band(KD):
- 80kD
- Background:
- This gene is a member of the synapsin gene family. Synapsins encode neuronal phosphoproteins which associate with the cytoplasmic surface of synaptic vesicles. Family members are characterized by common protein domains, and they are implicated in synaptogenesis and the modulation of neurotransmitter release, suggesting a potential role in several neuropsychiatric diseases. This member of the synapsin family plays a role in regulation of axonogenesis and synaptogenesis. The protein encoded serves as a substrate for several different protein kinases and phosphorylation may function in the regulation of this protein in the nerve terminal. Mutations in this gene may be associated with X-linked disorders with primary neuronal degeneration such as Rett syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SYN1 are a cause of epilepsy X-linked with variable learning disabilities and behavior disorders [MIM:300491]. XELBD is characterized by variable combinations of epilepsy, learning difficulties, macrocephaly, and aggressive behavior.,function:Neuronal phosphoprotein that coats synaptic vesicles, binds to the cytoskeleton, and is believed to function in the regulation of neurotransmitter release. The complex formed with NOS1 and CAPON proteins is necessary for specific nitric-oxid functions at a presynaptic level.,PTM:Substrate of at least four different protein kinases. It is probable that phosphorylation plays a role in the regulation of synapsin-1 in the nerve terminal. Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Belongs to the synapsin family.,subunit:Homodimer. Interacts with CAPON. Forms a ternary complex with NOS1. Isoform Ib interacts with
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell junction, synapse. Golgi apparatus .
- Expression:
- Brain,Brain cortex,
BDNF-Related Imbalance of Copine 6 and Synaptic Plasticity Markers Couples With Depression-Like Behavior and Immune Activation in CUMS Rats. Frontiers in Neuroscience Front Neurosci-Switz. 2018 Oct;0:731 WB Rat 1:1000 hippocampus,prefrontal cortex (PFC)
CRHR1 Mediates the Up-Regulation of Synapsin I Induced by Nesfatin-1 Through ERK 1/2 Signaling in SH-SY5Y Cells. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR NEUROBIOLOGY Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Apr;38(3):627-633 WB Human 1:1000 SH-SY5Y cell
Protective effect of quercetin against the metabolic dysfunction of glucose and lipids and its associated learning and memory impairments in NAFLD rats. Lipids in Health and Disease Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Dec;20(1):1-15 WB Rat 1:1000 Hippocampus
Resveratrol ameliorates learning and memory impairments induced by bilateral hippocampal injection of streptozotocin in mice NEUROCHEMISTRY INTERNATIONAL Cong-Cong Qi WB Mouse
Geniposide improves depression-like behavior in prenatal stress male offspring through restoring HPA axis- and glucocorticoid receptor-associated dysfunction LIFE SCIENCES Yu Ma WB Mouse hippocampal tissue
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
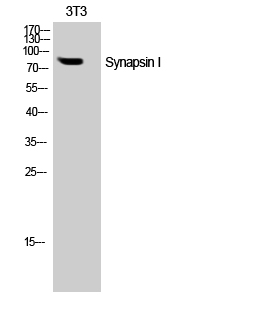
- Western Blot analysis of NIH-3T3 cells using Synapsin I Polyclonal Antibody

- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using Synapsin1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
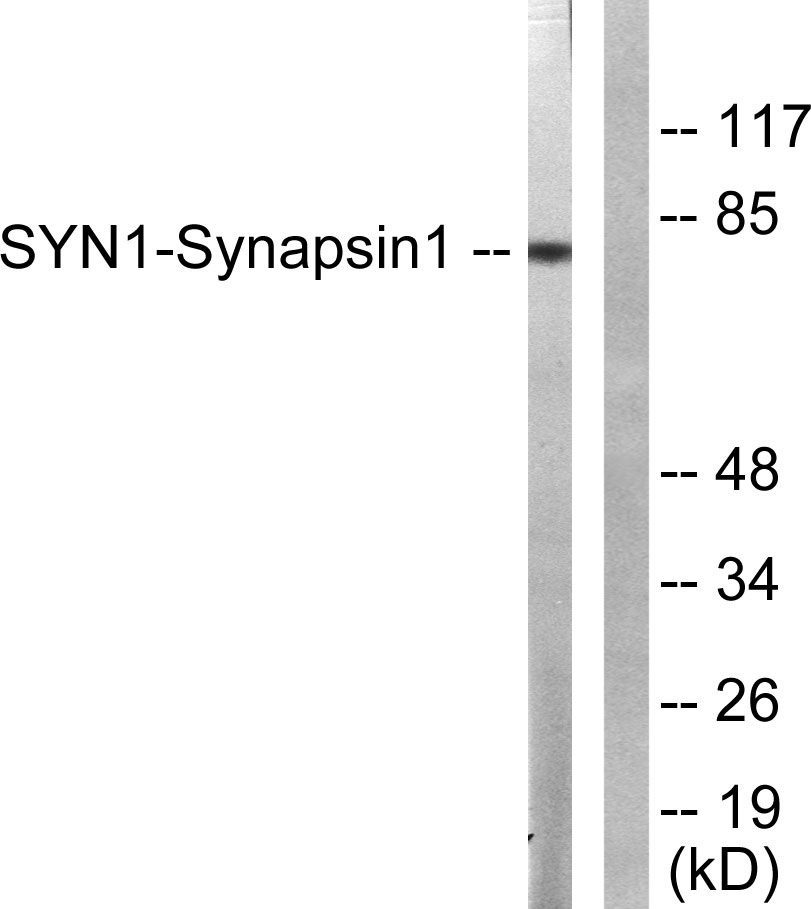
- Western blot analysis of lysates from NIH/3T3 cells, treated with Nocodazole 1ug/ml 16h, using Synapsin1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.