VASP (PT0347R) PT® Rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8205
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;IP;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- VASP
- Fields:
- >>Rap1 signaling pathway;>>cGMP-PKG signaling pathway;>>Focal adhesion;>>Tight junction;>>Platelet activation;>>Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis;>>Leukocyte transendothelial migration
- Gene Name:
- VASP
- Protein Name:
- Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein
- Human Gene Id:
- 7408
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P50552
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22323
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P70460
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal, rabbit, IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-1:1000,WB 1:1000-1:5000,IF 1:200-1:1000,ELISA 1:5000-1:20000,IP 1:50-1:200,
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- VASP;Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein;VASP
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 40kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 50kD
- Background:
- Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is a member of the Ena-VASP protein family. Ena-VASP family members contain an EHV1 N-terminal domain that binds proteins containing E/DFPPPPXD/E motifs and targets Ena-VASP proteins to focal adhesions. In the mid-region of the protein, family members have a proline-rich domain that binds SH3 and WW domain-containing proteins. Their C-terminal EVH2 domain mediates tetramerization and binds both G and F actin. VASP is associated with filamentous actin formation and likely plays a widespread role in cell adhesion and motility. VASP may also be involved in the intracellular signaling pathways that regulate integrin-extracellular matrix interactions. VASP is regulated by the cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases PKA and PKG. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:The EVH2 domain is comprised of 3 regions. Block A is a thymosin-like domain required for G-actin binding. The KLKR motif within this block is essential for the G-actin binding and for actin polymerization. Block B is required for F-actin binding and subcellular location, and Block C for tetramerization.,domain:The WH1 domain mediates interaction with XIRP1.,function:Ena/VASP proteins are actin-associated proteins involved in a range of processes dependent on cytoskeleton remodeling and cell polarity such as axon guidance and lamellipodial and filopodial dynamics in migrating cells. VASP promotes actin nucleation and increases the rate of actin polymerization in the presence of capping protein. Plays a role in actin-based activity of Listeria monocytogenes in platelets.,PTM:Major substrate for cAMP-dependent (PKA) and cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) in platelets. The preferred
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in platelets.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
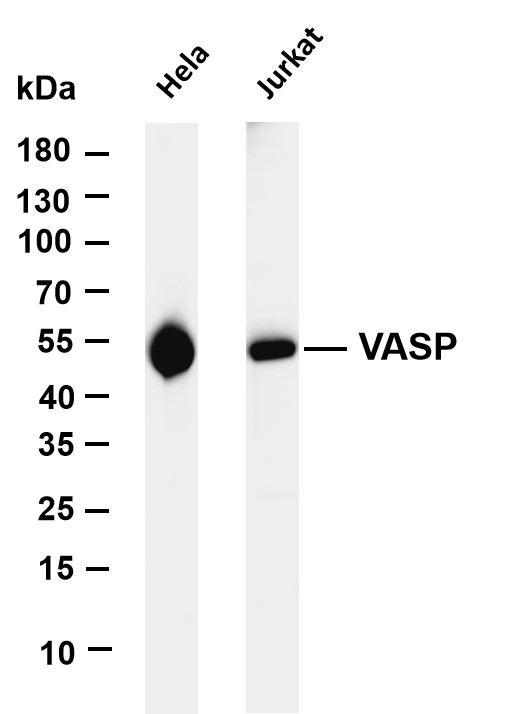
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-20% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-VASP (PT0347R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: Hela Lane 2: Jurkat Predicted band size: 40kDa Observed band size: 50kDa
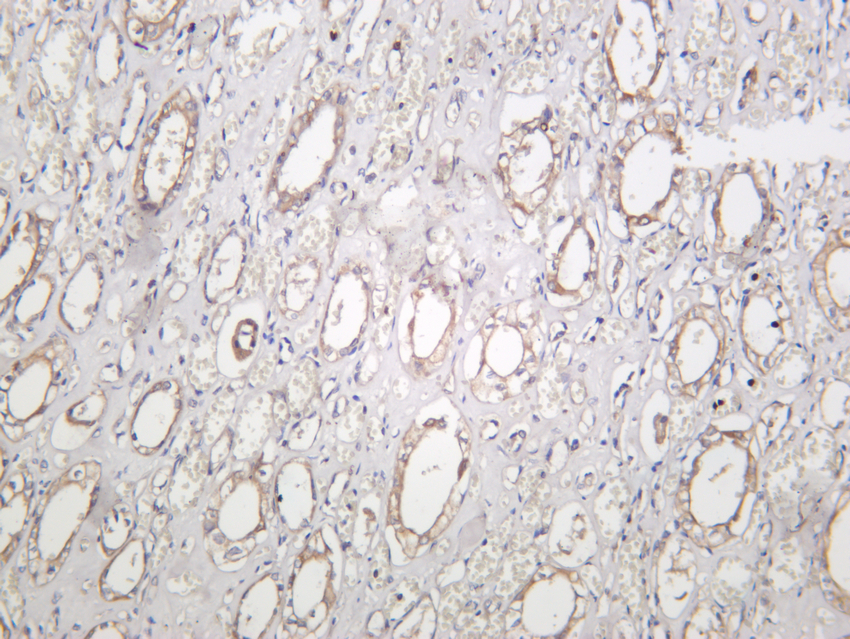
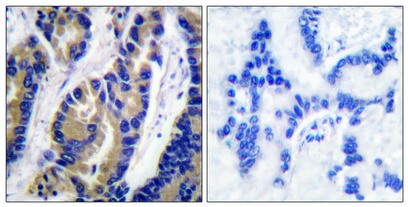
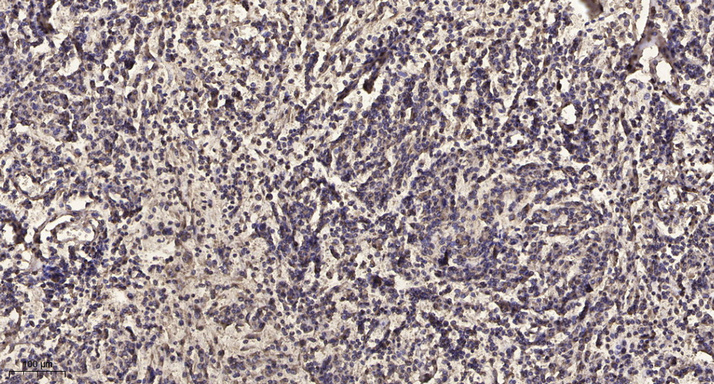
- Human kidney was stained with anti-VASP (PT0347R) rabbit antibody
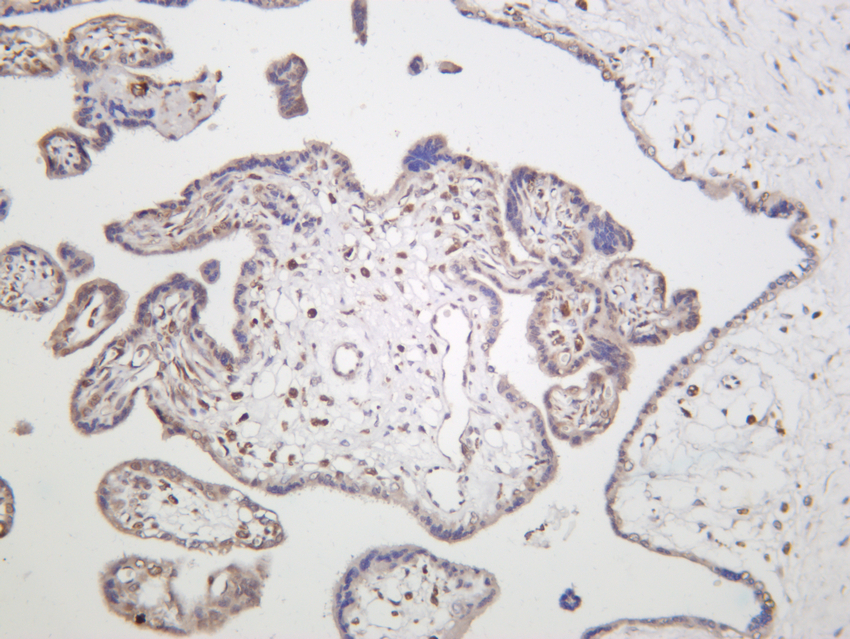
- Human placenta was stained with anti-VASP (PT0347R) rabbit antibody
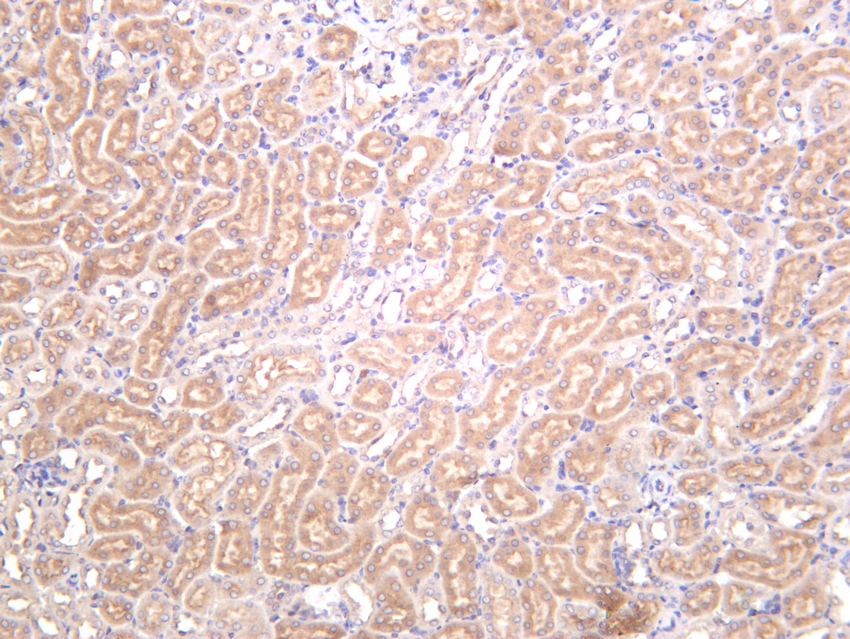
- Mouse kidney was stained with anti-VASP (PT0347R) rabbit antibody
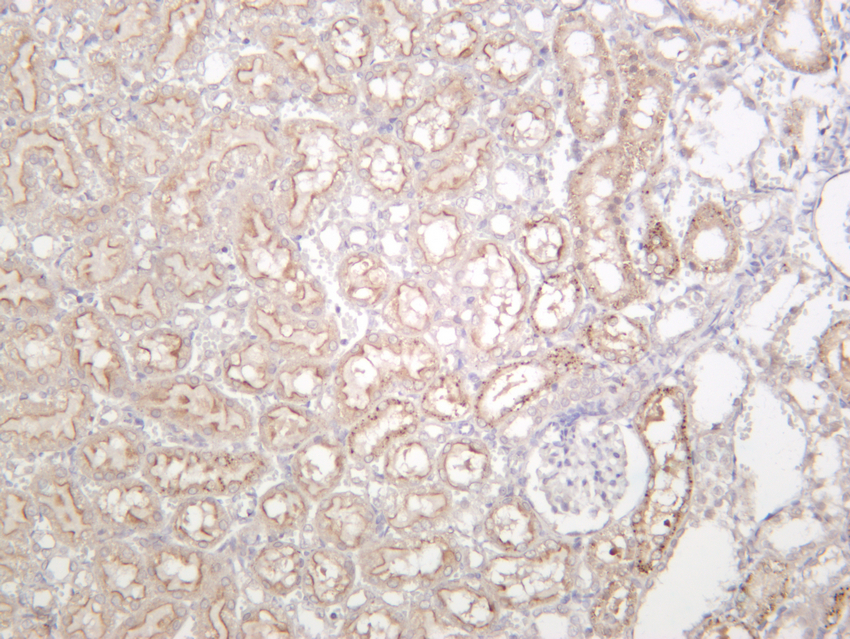
- Rat kidney was stained with anti-VASP (PT0347R) rabbit antibody