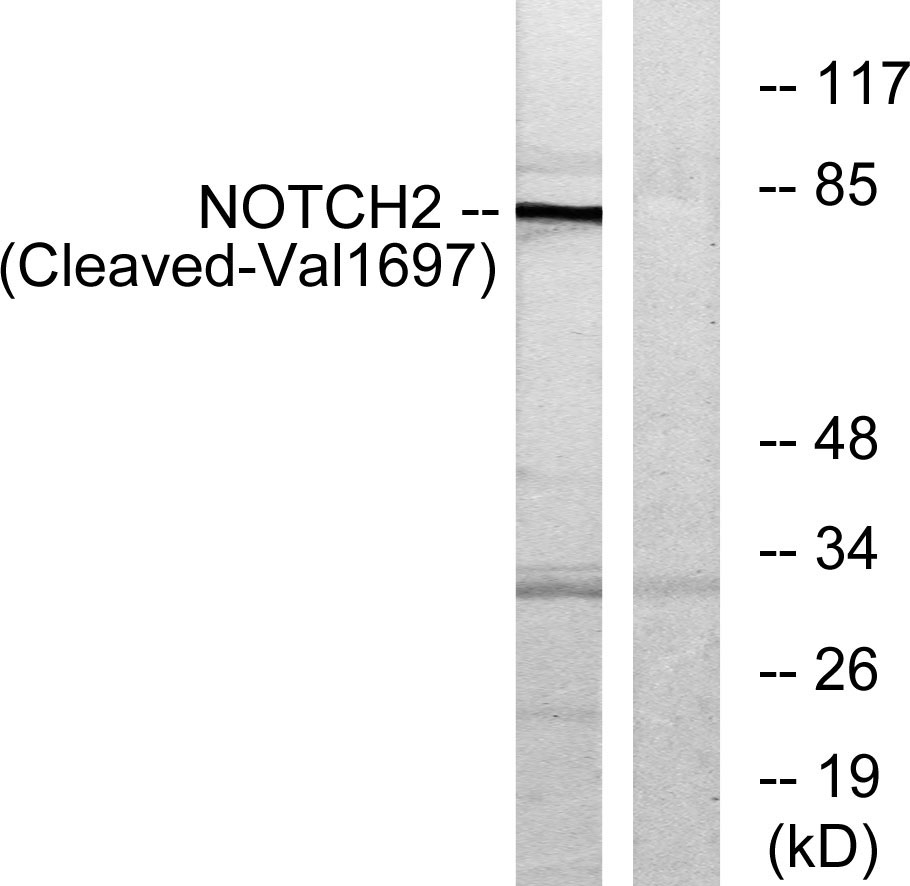
Cleaved-Notch 2 (A1734) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3970C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- NOTCH2
- Human Gene Id:
- 4853
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q04721
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O35516
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9QW30
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 (Notch 2) (hN2) [Cleaved into: Notch 2 extracellular truncation;Notch 2 intracellular domain]
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- disease:Defects in NOTCH2 are the cause of Alagille syndrome type 2 (ALGS2) [MIM:610205]. Alagille syndrome is an autosomal dominant multisystem disorder defined clinically by hepatic bile duct paucity and cholestasis in association with cardiac, skeletal, and ophthalmologic manifestations. There are characteristic facial features and less frequent clinical involvement of the renal and vascular systems.,function:Functions as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands Jagged1, Jagged2 and Delta1 to regulate cell-fate determination. Upon ligand activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) it forms a transcriptional activator complex with RBP-J kappa and activates genes of the enhancer of split locus. Affects the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs.,PTM:Phosphorylated.,PTM:Synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum as an inactive form which is proteolytically cleaved by a furin-like convertase in the trans-Golgi network before it reaches the plasma membrane to yield an active, ligand-accessible form. Cleavage results in a C-terminal fragment N(TM) and a N-terminal fragment N(EC). Following ligand binding, it is cleaved by TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) to yield a membrane-associated intermediate fragment called notch extracellular truncation (NEXT). This fragment is then cleaved by presenilin dependent gamma-secretase to release a notch-derived peptide containing the intracellular domain (NICD) from the membrane.,similarity:Belongs to the NOTCH family.,similarity:Contains 3 LNR (Lin/Notch) repeats.,similarity:Contains 35 EGF-like domains.,similarity:Contains 6 ANK repeats.,subcellular location:Following proteolytical processing NICD is translocated to the nucleus.,subunit:Heterodimer of a C-terminal fragment N(TM) and an N-terminal fragment N(EC) which are probably linked by disulfide bonds (By similarity). Interacts with MAML1, MAML2 and MAML3 which act as transcriptional coactivators for NOTCH2.,tissue specificity:Expressed in the brain, heart, kidney, lung, skeletal muscle and liver.,
- Function:
- cell fate determination, morphogenesis of an epithelium, morphogenesis of an epithelial sheet, immune system development, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, anti-apoptosis, induction of apoptosis, cell cycle, cell cycle arrest, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, Notch signaling pathway, determination of left/right symmetry, pattern specification process, negative regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of cell size,response to wounding, determination of symmetry, determination of bilateral symmetry, positive regulation of signal transduction, positive regulation of cell communication, regulation of cell death, positive regulation of cell death,induction of programmed cell death, cell growth, stem cell maintenance, cell cycle process, hemopoiesis, embryonic limb morphogenesis, regeneration, regulation of cellular component size, appendage morpho
- Subcellular Location:
- [Notch 2 extracellular truncation]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein .; [Notch 2 intracellular domain]: Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Following proteolytical processing NICD is translocated to the nucleus. Retained at the cytoplasm by TCIM (PubMed:25985737). .
- Expression:
- Expressed in the brain, heart, kidney, lung, skeletal muscle and liver. Ubiquitously expressed in the embryo.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
.jpg)

