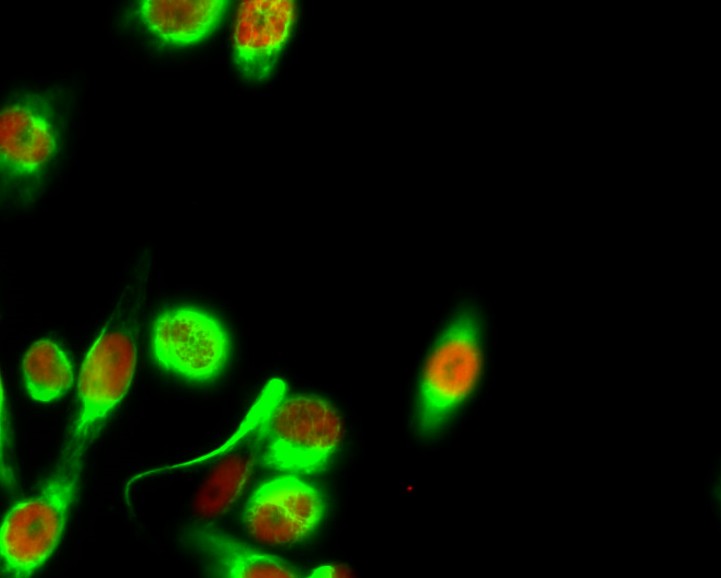
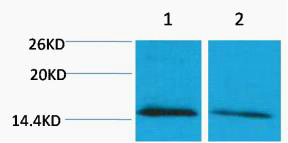
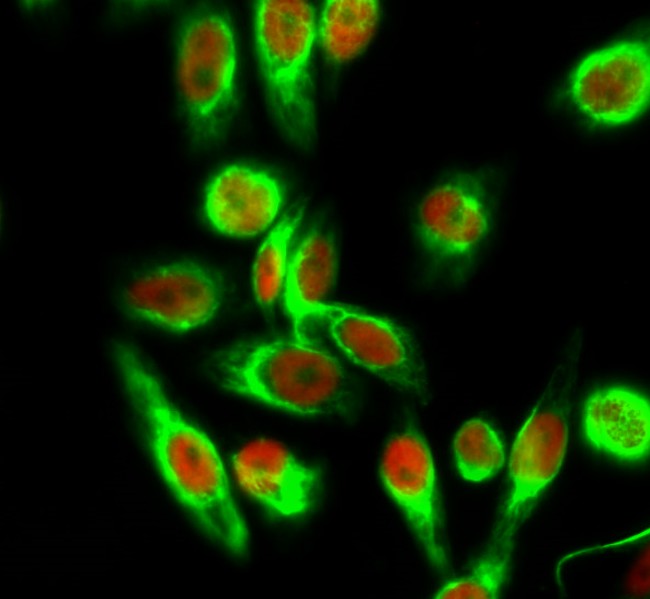
Total Histone H4 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3910C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H4A/HIST1H4B/HIST1H4C/HIST1H4D/HIST1H4E/HIST1H4F/HIST1H4H/HIST1H4I/HIST1H4J/HIST1H4K/HIST1H4L/HIST2H4A/HIST2H4B/HIST4H4
- Human Gene Id:
- 121504
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P62805
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P62806
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P62804
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Histone H4
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- function:Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.,PTM:Acetylation at Lys-6, Lys-9, Lys-13 and Lys-17 occurs in coding regions of the genome but not in heterochromatin.,PTM:Citrullination at Arg-4 by PADI4 impairs methylation.,PTM:Monomethylated, dimethylated or trimethylated at Lys-21. Monomethylation is performed by SET8. Trimethylation is performed by SUV420H1 and SUV420H2 and induces gene silencing.,PTM:Monomethylation at Arg-4 by PRMT1 favors acetylation at Lys-9 and Lys-13. Demethylation is performed by JMJD6.,PTM:Sumoylated, which is associated with transcriptional repression.,PTM:Ubiquitinated by the CUL4-DDB-RBX1 complex in response to ultraviolet irradiation. This may weaken the interaction between histones and DNA and facilitate DNA accessibility to repair proteins.,similarity:Belongs to the histone H4 family.,subunit:The nucleosome is a histone octamer containing two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assembled in one H3-H4 heterotetramer and two H2A-H2B heterodimers. The octamer wraps approximately 147 bp of DNA.,
- Function:
- DNA packaging, chromatin organization, chromatin assembly or disassembly, nucleosome assembly, intracellular signaling cascade, second-messenger-mediated signaling, chromatin assembly, cellular macromolecular complex subunit organization, cellular macromolecular complex assembly, nucleosome organization, macromolecular complex subunit organization, negative regulation of cell differentiation, regulation of myeloid cell differentiation, negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation, regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation, negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation, phosphoinositide-mediated signaling, chromosome organization, macromolecular complex assembly, protein-DNA complex assembly,
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Chromosome.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs